Fig. 9
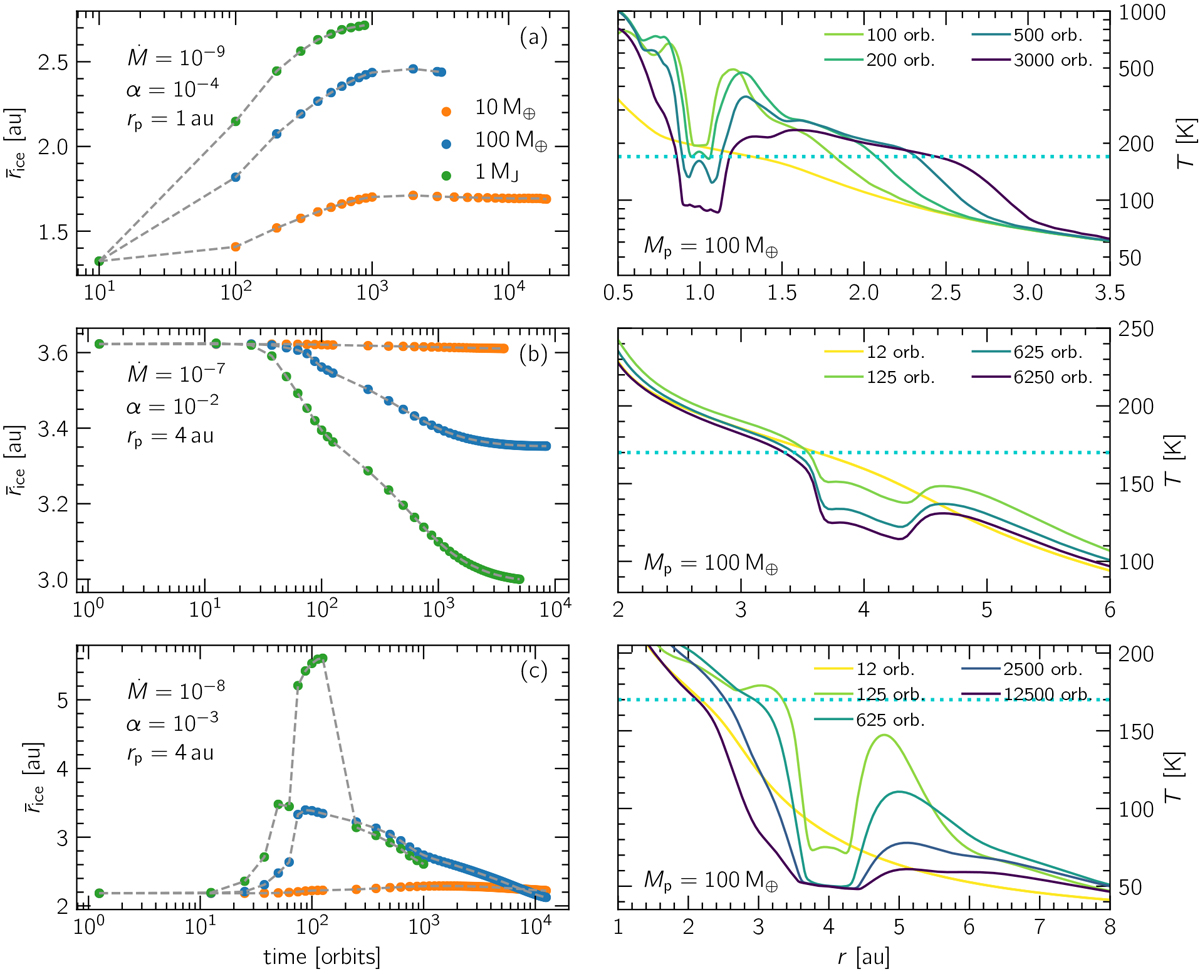
Azimuthally-averaged ice line location for three sample models, showcasing three possible evolution scenarios, panel a: spiral heating pushes ice line outwards; panel b: ice line recedes to the inner gap edge; panel c: shock heating initially pushes ice line outwards but eventually a gap is carved and ice line recedes inwards. These effects are amplified for more massive planets. It should be noted that in the case of a cold gap, ice can recondense within the gap region (panel a).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


