Fig. 7.
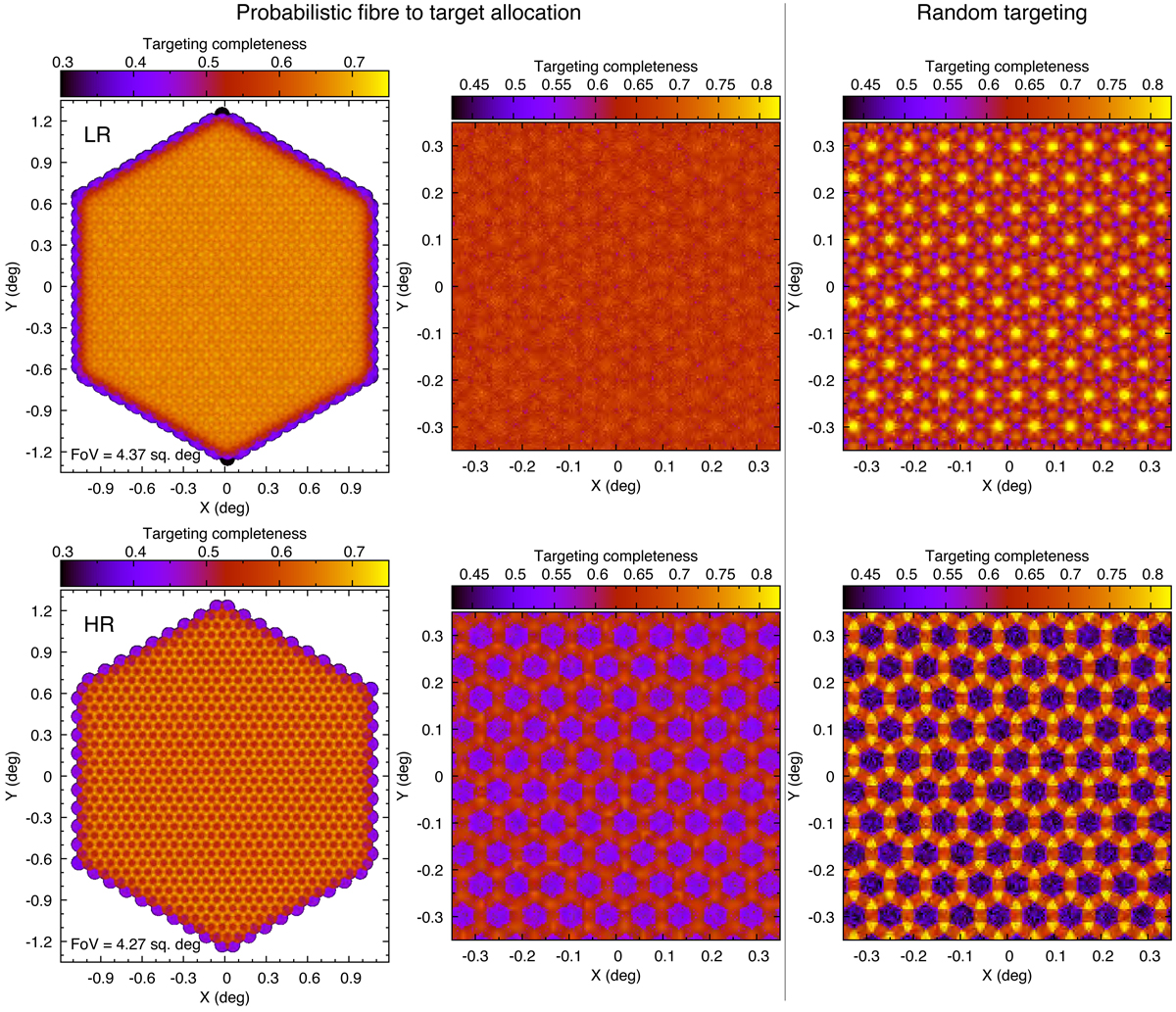
Targeting completeness in a single field of view. Top row: completeness map for low-resolution targets; bottom row: for high-resolution targets. In the targeting simulation, we used Poisson distributed targets across the sky with 1.5 times higher number density than the number density of fibres. Targeting was performed using the probabilistic fibre-to-target assignment as described in Sect. 2. Left panels: full field of view for a single field. The completeness decreases towards the edge of the field. Middle panels: zoom-in region of the left panel. For comparison, in the right panels we show a completeness map for random targeting in which each fibre-target pair has the same probability. In the right panel, we can clearly see the patrol regions of fibres (see also Fig. 1), which are significantly reduced when using probabilistic fibre-to-target assignment.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


