Fig. 3.
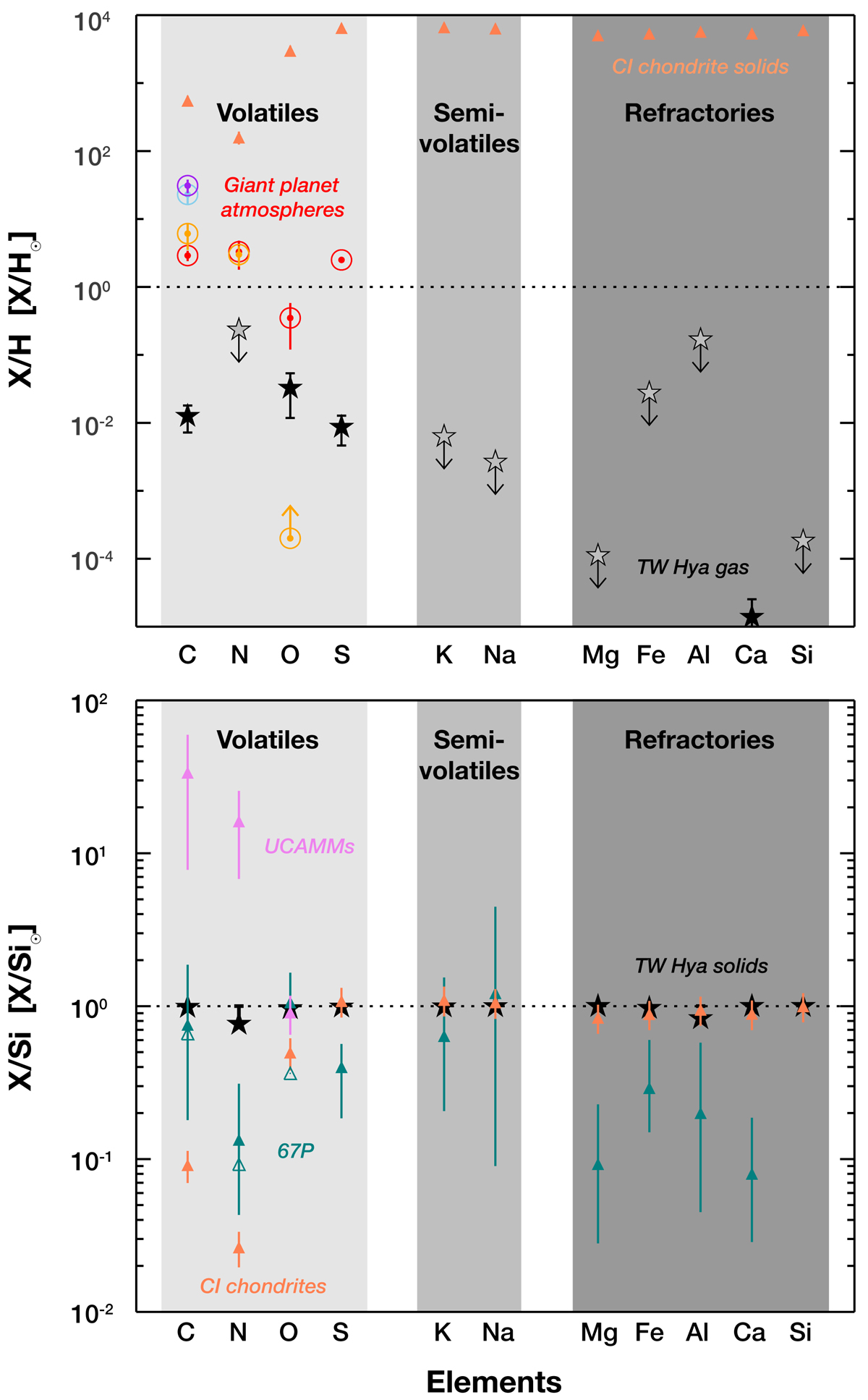
Top: comparison of bulk elemental gas abundances inside TW Hya’s dust sublimation rim (black stars, gray stars with arrows for upper limits), with atmospheric abundances of (Owen & Encrenaz 2003) Jupiter (red circles), Saturn (orange circles), Uranus (light blue circle), and Neptune (purple circle), and CI chondrite solids (Lodders 2010, salmon triangles). All data are plotted with error bars. Abundances are with respect to hydrogen and are normalized to the solar abundances (Asplund et al. 2009), with the solar value indicated by the dotted horizontal line. Bottom: comparison of bulk elemental abundances of solids for: TW Hya (black stars), CI chondrites (Lodders 2010, salmon triangles), comet 67P (bulk, dust/ice 1, teal triangles; Bardyn et al. 2017; Rubin et al. 2019), and UCAMMs (violet triangles; Dartois et al. 2017; Mathurin et al. 2019).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


