Fig. 3.
Download original image
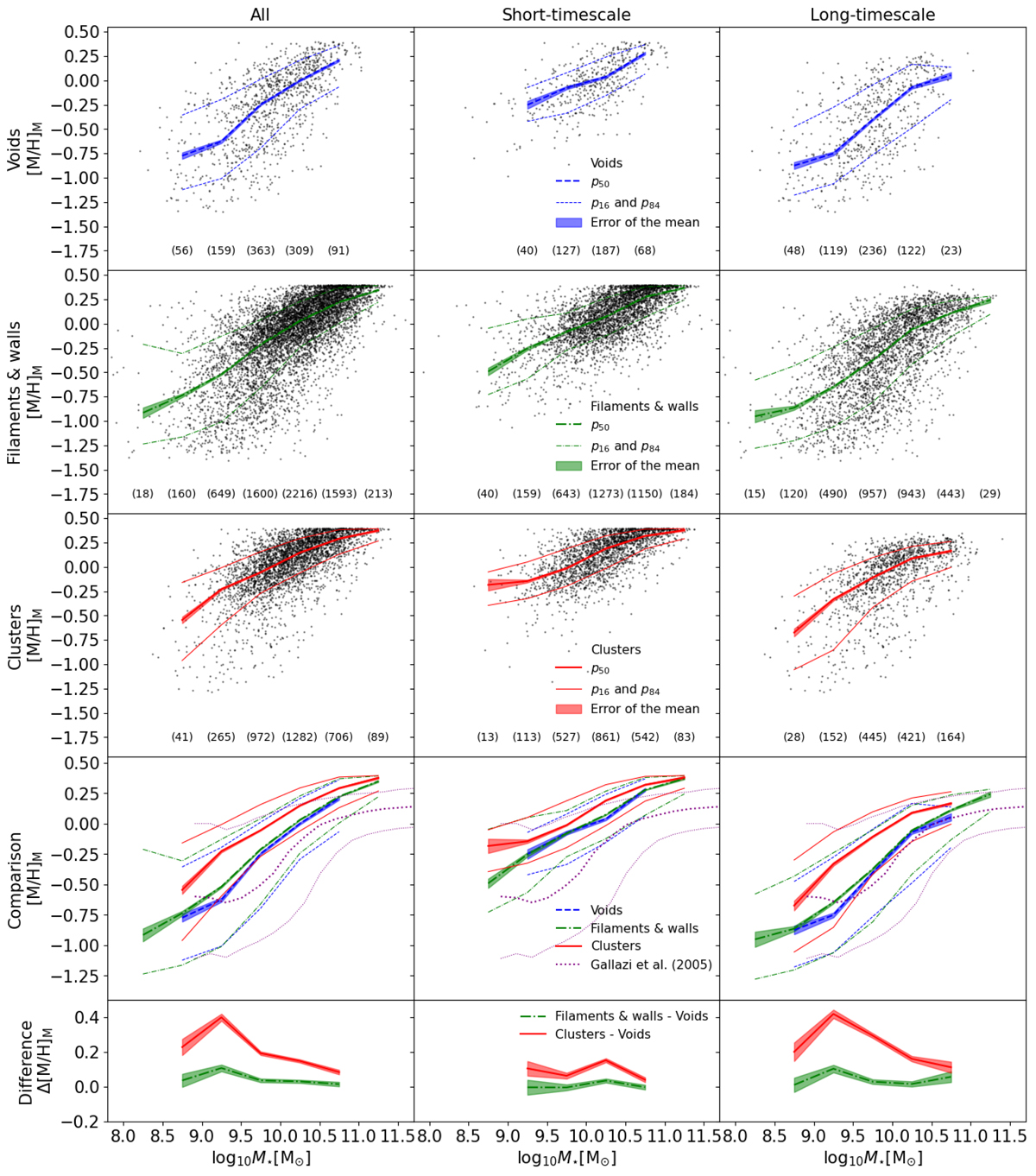
Stellar mass-metallicity relation (MZ⋆ R). Mass-weighted average stellar metallicity ([M/H]M) as a function of the total stellar mass for the galaxies regardless of their SFH type (left column), galaxies with ST-SFHs (centre column), and galaxies with LT-SFHs (right column) in voids (first row), filaments & walls (second row), and clusters (third row). The MZ⋆ R (dashed blue lines for voids, dot-dashed green lines for filaments & walls, and solid red lines for clusters) is derived as the 50th percentile (thick lines) inside each stellar mass bin of 0.5 dex. The number of galaxies inside each stellar mass bin is shown in brackets at the bottom of the panels. The shaded areas represent the s.e.m., and the 16th and 84th percentiles (thin lines) show the dispersion of the MZ⋆ R. The fourth row shows a comparison of the MZ⋆ R between galaxies voids, filaments & walls, and clusters, together with the MZ⋆ R from Gallazzi et al. (2005) as a reference. In the fifth row, we show the differences of the MZ⋆ R (lines), together with the error of the difference (shaded areas). See the values reported in Tables E.1 and E.2.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


