Fig. 1.
Download original image
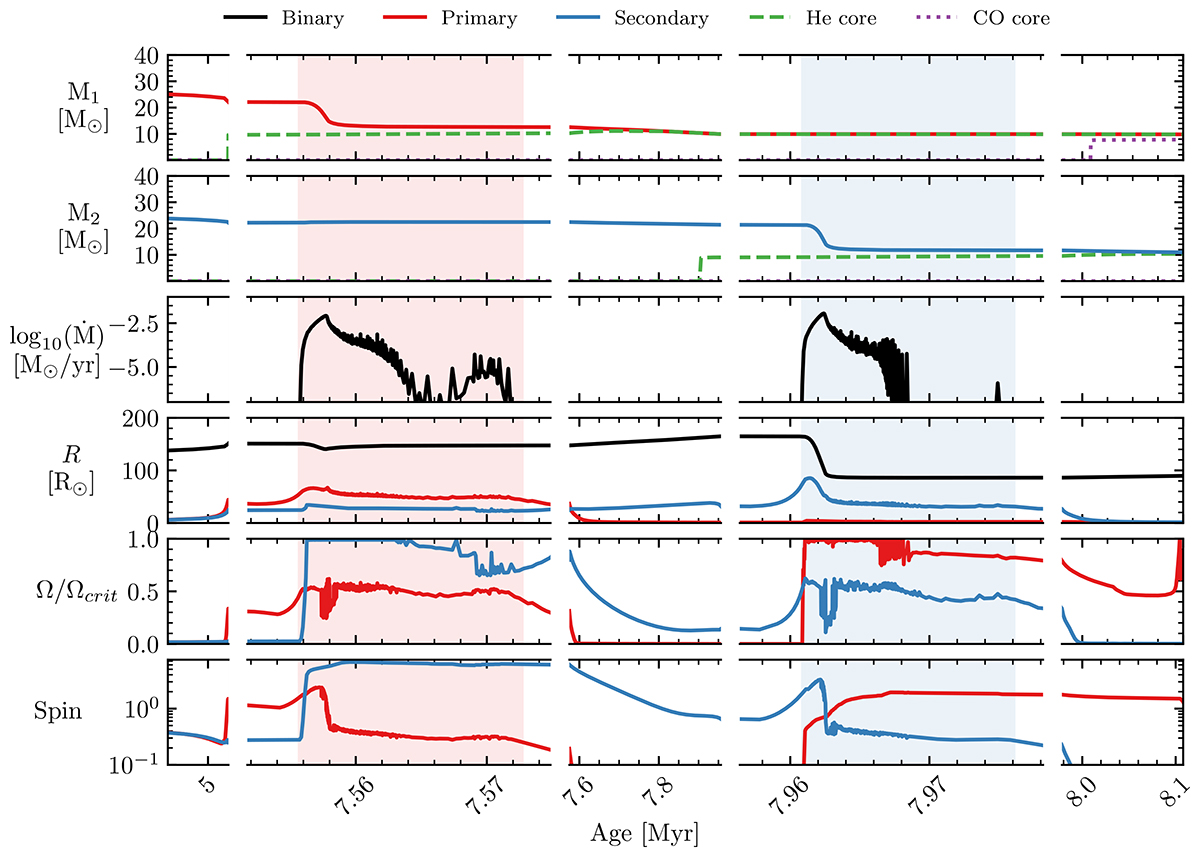
Typical example of the evolution of a potential LGRB progenitor through the stable reverse-mass-transfer channel. The initial properties of the binary are Z = Z⊙, M1, ZAMS ≈ 25.1 M⊙, q = 0.95, and P ≈ 26.8 days. In all panels, red (blue) solid lines refer to the primary (secondary) star. The columns are split into five different evolutionary phases, focusing on the mass transfer phases. The second and fourth columns show the mass transfer and ‘reverse’ mass transfer phases, respectively. The first, third and last columns show the long, nuclear timescale, detached evolution of the system. Top two rows: Total mass (solid lines), He core mass (dashed lines) and CO core mass (dotted lines). The He (CO) core boundaries are set where the hydrogen (helium) fraction falls below 0.1. Third row: Mass transfer rate from Roche lobe overflow. The periods of Roche lobe overflow are marked by a red (blue) shading when the donor is the primary (secondary). Fourth row: Evolution of stellar radius (red: primary; blue: secondary) and separation of the system (black). Fifth row: Surface rotational angular frequency in units of the critical (i.e., mass shed) value. Sixth row: the dimensionless spin parameter cJ/GM2 of the star.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


