Fig. 3.
Download original image
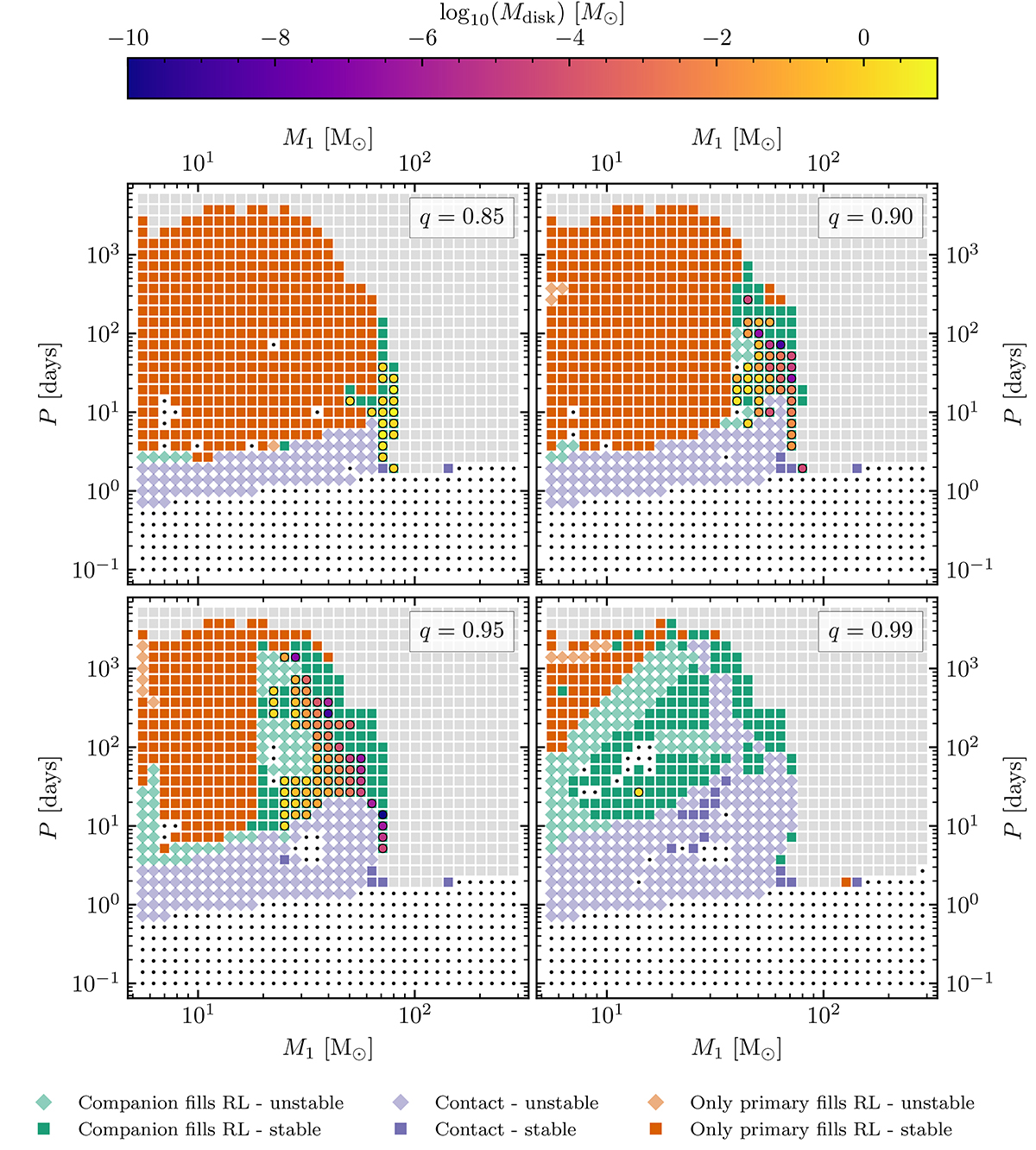
Four grid slices at Z⊙ with q = 0.85, 0.90, 0.95, and 0.99. Orange symbols represent systems where only the primary fills its Roche lobe throughout the evolution of the binary model. Green squares indicate systems where also the secondary fills its Roche lobe, but not at the same time as the primary. Purple symbols indicate systems where both stars fill their Roche lobe at the same time. The type of symbol shows the stability of the interaction: squares indicate stable mass transfer, while binary models reaching instability criteria are indicated with a diamond. Gray squares indicate no mass transfer, while black dots indicate a non-converged model or Roche lobe overflow when the model is initiated. For systems where the companion fills its Roche lobe and the interaction remains stable, we indicate if an accretion disk is formed during the collapse of the model. This is indicated by a coloured circle inside the square symbol, where the colour indicates the mass of the accretion disk.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


