Fig. 6
Download original image
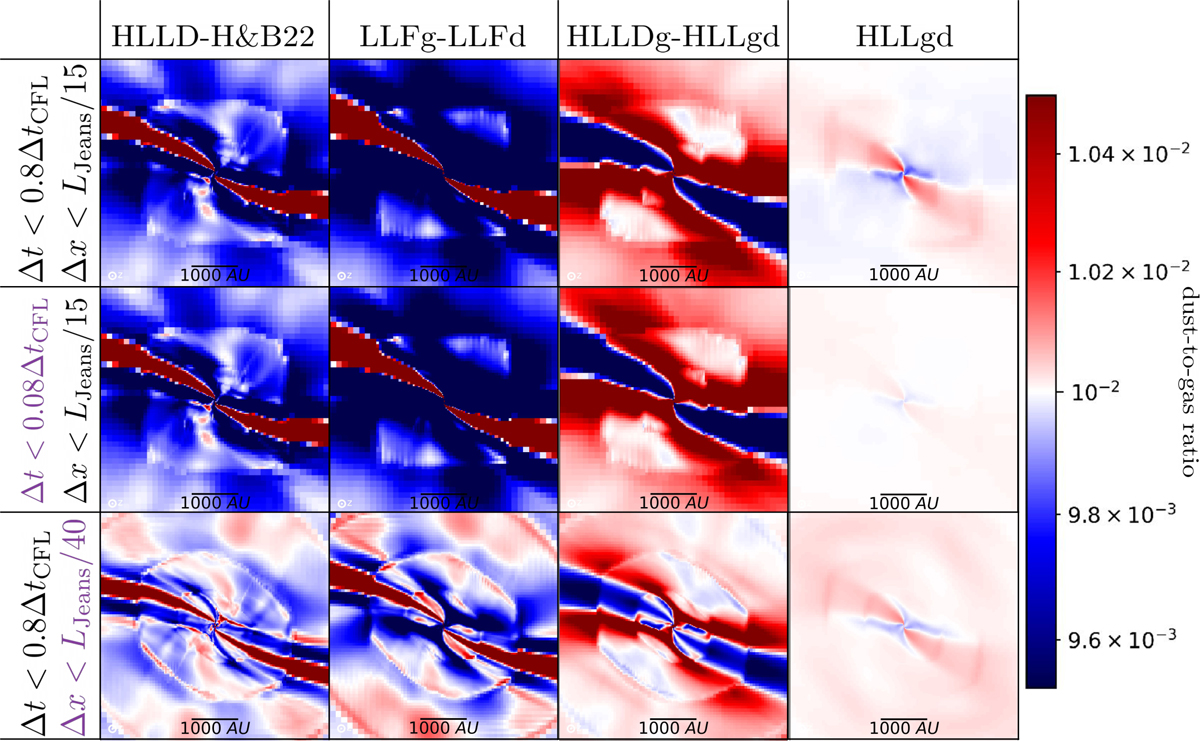
Collapse simulations with the multifluid implementation for different Riemann solvers (columns) and for different spatial and time resolution (lines), expressed by the safety factor of the CFL condition and the number of Jeans length per cells for the mesh refinement. HLLD is from Miyoshi & Kusano (2005), H&B22 stands for the Riemann solver from Huang & Bai (2022), HLLDg-HLLgd means that we use the HLLD solver for the gas and the HLLgd solver only for the dust multifluid. We choose the same colorbar scale and box size as Fig. 5 in order to compare to the terminal velocity approximation. However, for the three first solvers, some regions are saturated: for the low-resolution runs, the dust-to-gas ratio (divided by 10–2) in these regions vary from 0.9 to 1.2 for HLLD-H&B22, from 0.75 to 1.3 for the LLFg-LLFd, and from 0.9 to 1.5 for HLLDg-HLLgd.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


