Fig. 5.
Download original image
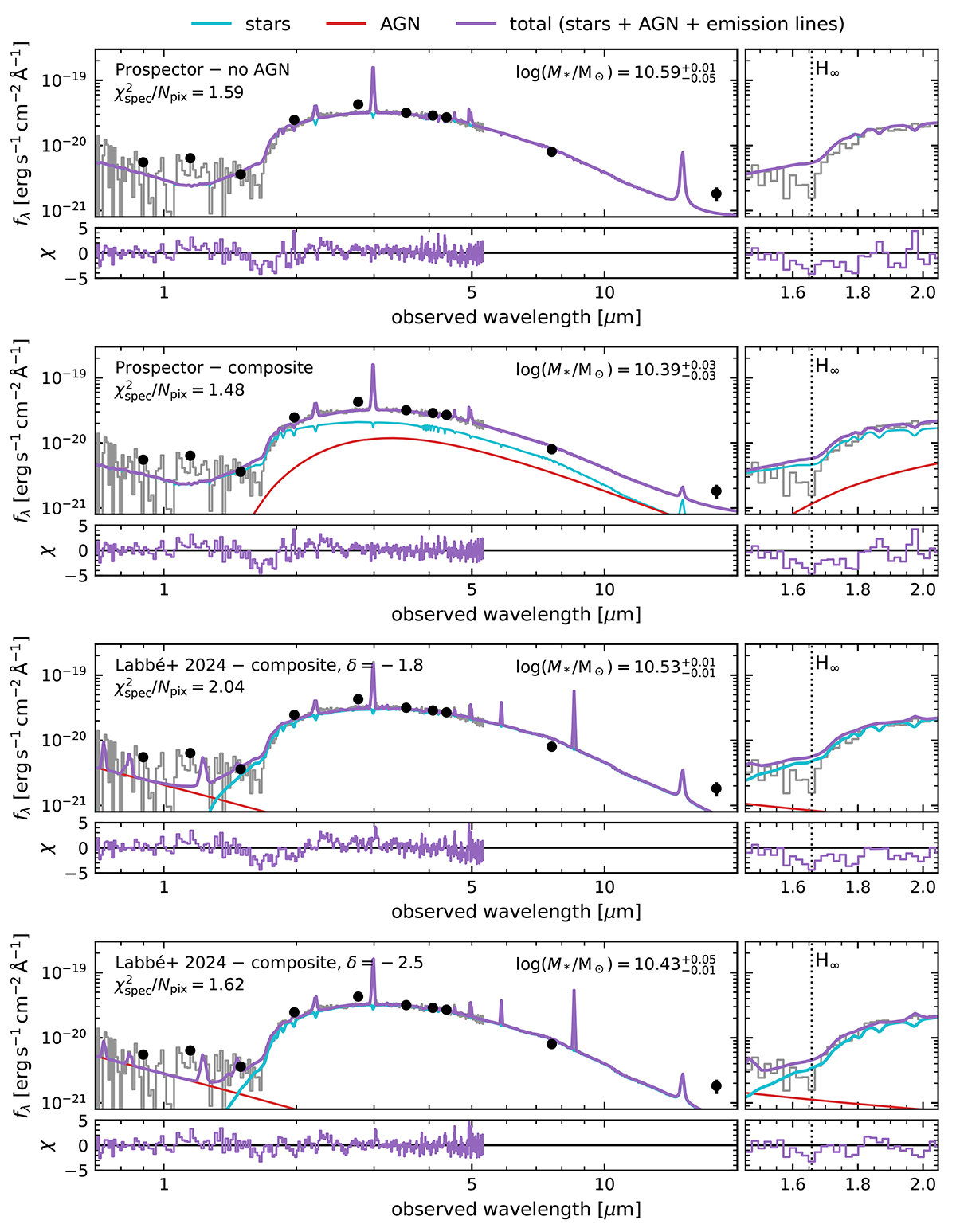
Best-fit SED models and residuals (with respect to the PRISM spectrum) for four model variations, constructed as different mixtures of (dust-reddened) stellar population and power-law AGN model components. These AGN models do not consider the possible reddening by absorbing dense gas, which we explore in Section 6.4. The right panels show zoomed-in images of the region around the Balmer break. From top to bottom: the fiducial galaxy-only model from Prospector; a galaxy + AGN model that maximises the stellar contribution, fit with Prospector (the maximal M* model of Wang et al. 2024a); the galaxy + AGN model following Labbe et al. (2024), but fitting only hydrogen emission lines instead of a forest of metal lines; the galaxy + AGN model of Labbe et al. (2024), but with an even steeper dust law (see Section 6.1). All four models favour a massive post-starburst solution, with a very steep dust attenuation law and high optical depth. However, even with such extreme dust, none of these models can produce the strong Balmer break and shape of the rest-frame optical SED, as is evident from the systematic (and significant) features in the residuals blueward and redward of the Balmer break.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


