Fig. 8.
Download original image
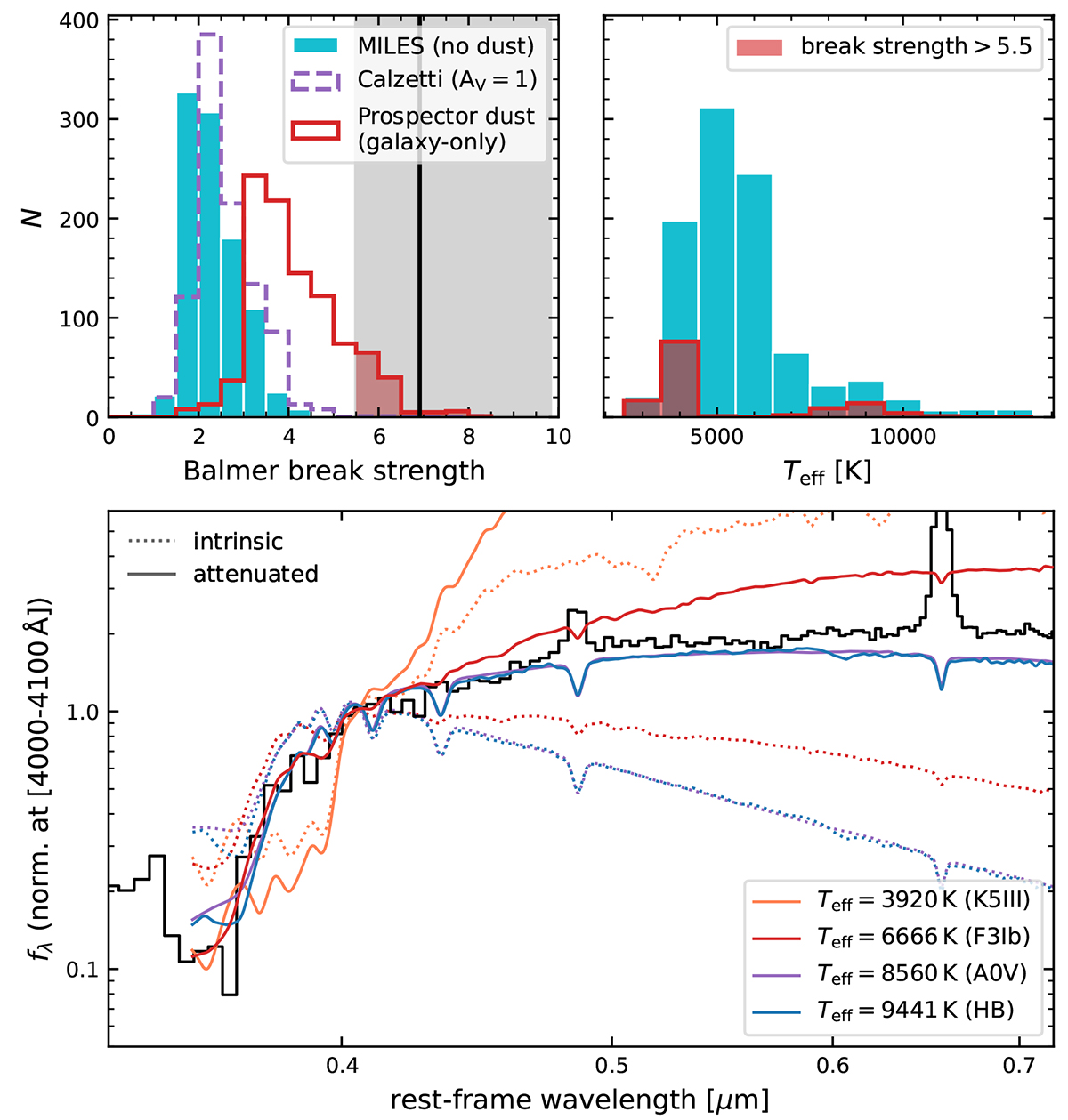
Top left: Balmer break strength (from rest-frame [3620,3720] Å and [4000,4100] Å ranges) distribution for the standard MILES stellar library (blue), and after applying a Calzetti dust law (with AV = 1; dashed purple), and the steep attenuation law from the Prospector galaxy-only model (solid red). The black vertical line and shaded region show the measured break strength and 1σ uncertainty of The Cliff. Top right: Effective temperatures of all MILES stars (blue) and the stars that, after applying the steep dust law, fall within 1σ of The Cliff (red). Bottom: Representative sample of MILES spectra with strong Balmer breaks, convolved to the PRISM resolution at z = 3.5 and normalised at [4000,4100] Å. Dotted and solid lines show the stellar spectra without dust and with steep dust attenuation, respectively. In comparison to the spectrum of The Cliff, K giants, main-sequence A stars and horizontal branch stars fall short at <3645 Å and >5000 Å. Only massive supergiants with steep dust attenuation can match the strength and shape of the Balmer break (albeit with a mismatch at > 5000 Å), and suggests that an extraordinary, top-heavy IMF would be required to explain the rest-frame optical emission of The Cliff.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


