Fig. 1
Download original image
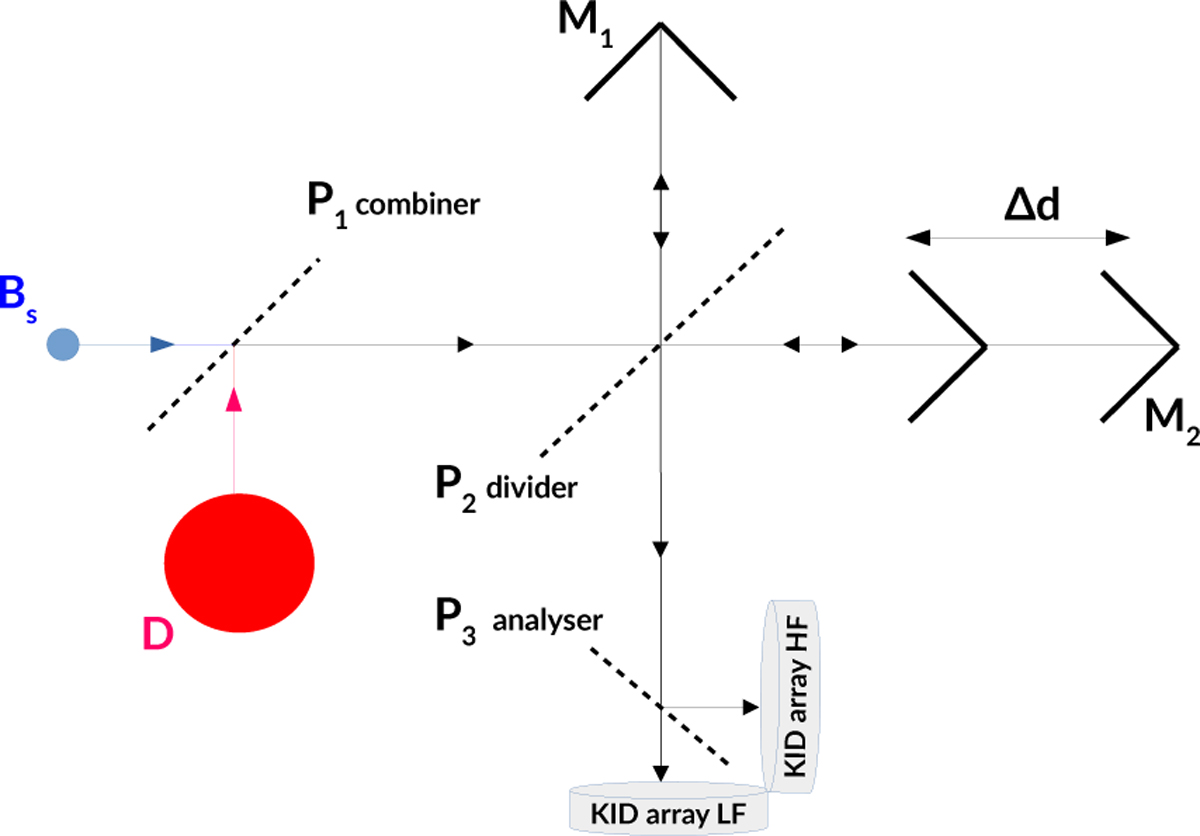
CONCERTO MPI optical concept. The main beams, Bp and Bs, described in Eqs. (3) and (4), enter the first input port of the MPI, while an unfocussed disc (D) enters the second port. A first polarizing grid, P1, is at the entrance of the MPI. A second grid, P2, divides the light between the two MPI arms, each ending at a rooftop mirror (two plane mirrors at 90 deg. angle), M1 or M2. Mirror M1 is fixed, whereas M2 oscillates along the horizontal axis, providing a variable OPD of 2Δd. Grid P2 then recombines the light and sends it into the cryostat. The light is analysed by a third polarizing grid, P3, which provides the two MPI output ports feeding two KID arrays, LF and HF. Each spectral component (ν) of the incoming radiation interferes constructively or destructively, depending on the moving-mirror position (Δd). The total output signal on one detector, S (Δd), is the integral over the entire wavelength range of the input spectra, modulated by the OPD between the two arms. By performing a Fourier transform of this signal as a a function of Δd, the spectral intensity, Iv, of the incoming radiation can be recovered, enabling precise spectroscopic analysis.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


