Table B.1.
Lens mass models.
| Model Name | Description | Number of mass parameters Npar | χim, MP2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| variable | with Gaussian priors | |||
| iso_halo | 25 | 4 | 6.3 | |
| • primary cluster DM halo: isothermal elliptical mass distribution | 6 | 0 | ||
| • perturbative cluster DM halo: isothermal elliptical mass distribution | 6 | 0 | ||
• cluster members scaling relation for 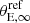 and and 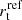 , with Gaussian prior on velocity dispersion based on Faber-Jackson , with Gaussian prior on velocity dispersion based on Faber-Jackson |
2 | 1 | ||
| • circular BCG with Gaussian prior on θE, ∞, BCG from velocity-dispersion measurement and uniform prior on rt, BCG | 2 | 1 | ||
| • cluster member IDphot 116 with Gaussian prior on θE, ∞, 116 from velocity-dispersion measurement and uniform prior on rt, 116 | 2 | 1 | ||
| • three jellyfish galaxies with variable Einstein radii | 3 | 0 | ||
| • foreground LOS galaxy at zfg = 0.309 with variable θE, ∞, fg and rt, fg | 2 | 0 | ||
| • background LOS galaxy at zbg = 0.371 with θE, ∞, bg having prior from velocity dispersion and variable rt, bg with uniform prior | 2 | 1 | ||
| PL_halo | 26 | 4 | 6.3 | |
| • primary cluster DM halo: power-law elliptical mass distribution | 7 | 0 | ||
| • other components are the same as the iso_halo model above | 19 | 4 | ||
| NFW_halo | 25 | 4 | 23 | |
| • primary cluster DM halo: elliptical NFW mass distribution | 6 | 0 | ||
| • other components are the same as the iso_halo model above | 19 | 4 | ||
| iso_halo+sheet | 26 | 4 | 6.3 | |
| • same components as the iso_halo model above | 25 | 4 | ||
| • mass-sheet parameter | 1 | 0 | ||
| iso_halo+ell_BCG | 27 | 4 | 5.7 | |
| • same components as the iso_halo model, excluding the BCG (elliptical instead of circular) | 23 | 3 | ||
| • elliptical BCG with Gaussian prior on θE, ∞, BCG from velocity-dispersion measurement and uniform priors on rt, BCG, qBCG and ϕBCG | 4 | 1 | ||
| single_plane | 25 | 4 | 6.1 | |
| • same components as the iso_halo model above except the foreground galaxy (at zfg = 0.309) and background galaxy (at zbg = 0.371) are assumed to be at the cluster redshift of zd = 0.336. The positional uncertainties of the multiple image positions are elliptical, as listed in Table 4 and used in the above models. | 25 | 4 | ||
| baseline | 25 | 4 | 7.3 | |
• same components as the single_plane model above except the positional uncertainties of the multiple image positions are circularized from the elliptical uncertainties. The circularized uncertainty is taken to be the geometric mean of the semi-major and semi-minor axis of the elliptical uncertainty (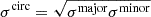 ). ). |
25 | 4 | ||
Notes. The first line of each model lists the total number of parameters, whereas the subsequent lines indicate the numbers of parameters for the specific components of the mass model. The last column (χim, MP2) is the image-position χ2 of the most-probable mass model. The galaxy mass centroids are located at their observed light centroids, and the galaxies are assumed to be circular, except for the BCG where we considered both circular and elliptical mass distributions. Therefore, all galaxies following the scaling relations are described by two parameters (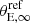 and
and 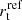 ), whereas galaxies not following the scaling relations have each two parameters (θE, ∞, i and rt, i for galaxy i) when they are circular, and four parameters (θE, ∞, BCG, rt, BCG, qBCG and ϕBCG) when elliptical. The number of free parameters for the DM halo parametrizations is described in Sect. 5.1.2 and 5.1.3 and listed in the table.
), whereas galaxies not following the scaling relations have each two parameters (θE, ∞, i and rt, i for galaxy i) when they are circular, and four parameters (θE, ∞, BCG, rt, BCG, qBCG and ϕBCG) when elliptical. The number of free parameters for the DM halo parametrizations is described in Sect. 5.1.2 and 5.1.3 and listed in the table.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


