Table 3.
Terms associated with the variation of the orbital period.
| YMW16 | NE2001 | |
|---|---|---|
| (fs s−1) | ||
| Ṗb,obs | −1829.6(15) | |
| Ṗb,GR | −1828.7(1) | |
| ΔṖb |
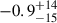 |
|
| Ṗb,gal | −1.93(62) | −2.46(68) |
| Ṗb,shk | +1.05(23) | +1.25(28) |
| Ṗb,ext | −0.88(66) | −1.21(74) |
| Ṗb,int | −1828.8(16) | −1828.4(16) |
| Ṗb,xs | −0.1(16) | +0.3(16) |
Notes. The term ΔṖb = Ṗb,obs − Ṗb,GR represents a constraint on the sum external contributions to Ṗb, this is calculated in detail in Sect. 4.1; this value is represented by the gray bar in Fig. 6. The sum of the external contributions calculated by our models for the two assumed distances, Ṗb,ext = Ṗb,gal + Ṗb,shk, are in good agreement with ΔṖb (see red band in Fig. 6). The intrinsic Ṗb, Ṗb,int is defined as Ṗb,obs − Ṗb,gal − Ṗb,shk; if GR is correct, this should match Ṗb,GR. The difference between Ṗb,int and Ṗb,GR is the “excess” variation of the orbital period, Ṗb,xs which quantifies possible deviations from GR.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


