Table A.1.
Physical properties for the lens samples included in the joint lensing+kinematics cosmology inference.
| Lens | zlens | zsource | 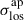 [km s−1] [km s−1] |
Reff [″] | θE [″] | γpl | qlight | ℐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DES J0408−5354 | 0.597 | 2.375 | 242.3±12.2 | 1.940 | 1.92 | 1.90±0.03 | 0.80 | – |
| HE 0435−1223 | 0.455 | 1.693 | 226.6±5.8 | 1.800 | 1.22 | 1.93±0.02 | 0.93 | – |
| PG 1115+080 | 0.311 | 1.722 | 235.7±6.6 | 0.450 | 1.08 | 2.17±0.05 | 0.95 | – |
| RX J1131−1231 | 0.295 | 0.654 | 303.0±8.3 | 1.910 | 1.63 | 1.95±0.05 | 0.94 | – |
| SDSS J1206+4332 | 0.745 | 1.789 | 290.5±9.5 | 0.290 | 1.25 | 1.95±0.05 | 0.85 | – |
| B1608+656 | 0.630 | 1.394 | 305.3±11.0 | 0.590 | 0.81 | 2.08±0.03 | 1.00 | – |
| WFI 2033−4723 | 0.657 | 1.662 | 210.7±10.5 | 1.970 | 0.94 | 1.95±0.02 | 0.83 | – |
| WGD 2038−4008 | 0.228 | 0.777 | 254.7±16.3 | 2.223 | 1.38 | 2.30±0.02 | 0.85 | – |
| SDSS J0029−0055 | 0.227 | 0.931 | 208.2±2.8 | 2.386 | 0.94 | 2.69±0.25 | 0.94 | 128.3 |
| SDSS J0037−0942 | 0.195 | 0.632 | 278.8±2.9 | 3.334 | 1.48 | 2.38±0.11 | 0.87 | 240.1 |
| SDSS J1112+0826 | 0.273 | 0.629 | 276.4±3.4 | 1.623 | 1.50 | 1.92±0.18 | 0.76 | 254.9 |
| SDSS J1204+0358 | 0.164 | 0.631 | 260.2±2.9 | 1.544 | 1.29 | 2.02±0.05 | 0.99 | 204.9 |
| SDSS J1250+0523 | 0.232 | 0.795 | 243.4±2.6 | 1.748 | 1.12 | 2.18±0.09 | 0.92 | 225.1 |
| SDSS J1306+0600 | 0.173 | 0.472 | 229.7±2.8 | 2.369 | 1.31 | 1.97±0.07 | 0.88 | 121.1 |
| SDSS J1402+6321 | 0.205 | 0.481 | 282.6±2.9 | 2.720 | 1.37 | 1.57±0.30 | 0.76 | 56.5 |
| SDSS J1531−0105 | 0.160 | 0.744 | 275.8±3.6 | 3.416 | 1.71 | 2.07±0.26 | 0.85 | 118.7 |
| SDSS J1621+3931 | 0.245 | 0.602 | 262.7±3.5 | 2.402 | 1.27 | 2.02±0.07 | 0.87 | 265.2 |
| SDSS J1627−0053 | 0.208 | 0.524 | 263.5±3.3 | 2.981 | 1.22 | 1.93±0.14 | 0.92 | 185.6 |
| SDSS J1630+4520 | 0.248 | 0.793 | 279.4±3.1 | 2.012 | 1.79 | 1.92±0.09 | 0.83 | 161.2 |
| SL2SJ0226−0420 | 0.494 | 1.230 | 310.0±14.0 | 0.389 | 1.15 | 2.05±0.15 | 0.73 | 224.1 |
| SL2SJ0855−0147 | 0.365 | 3.390 | 196.0±11.0 | 0.470 | 0.96 | 2.25±0.11 | 0.91 | 177.5 |
| SL2SJ0904−0059 | 0.611 | 2.360 | 232.0±9.0 | 0.713 | 1.41 | 1.98±0.15 | 0.81 | 319.7 |
| SL2SJ2221+0115 | 0.325 | 2.350 | 277.0±13.0 | 0.532 | 1.27 | 2.14±0.13 | 0.77 | 195.3 |
Notes. From top to bottom, the time-delay TDCOSMO-2025 lenses, the SLACS sample, and the SL2S sample are separated by horizontal dividers. From left to right, the listed quantities are: deflector redshift zlens, background source redshift zsource, stellar velocity dispersion measured within an aperture σlosap, half-light radius Reff, Einstein radius θE, lensing power-law slope γpl, observed axis ratio of light profile of the deflector qlight, and lensing information ℐ calculated by Sheu et al. (2025). The uncertainties in the stellar velocity dispersions σlosap include both statistical and systematic uncertainties, summed in quadrature. For the lenses with IFU kinematic data (RX J1131−1231 and the quality SLACS sample), we list the deflector’s stellar velocity dispersion σlosap measured within apertures with radii equal to half the effective radii (Table 2 in Knabel et al. 2025a) for comparison with lenses with aperture stellar velocity dispersions. The stellar velocity dispersion σlosap for the SL2S sample is taken from Mozumdar et al. (2025). For the half-light radius Reff, we estimated the uncertainty to be 5% in the inference. For the Einstein radius θE, we estimated the uncertainty to be 2%. For lenses with aperture kinematic data, the uncertainty for the lensing power-law slope γpl was marginalized over in the inference. For the SLACS lenses with velocity dispersion profiles from spatially resolved data, the power-law slope inference is driven by the kinematic data.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


