Fig. 2.
Download original image
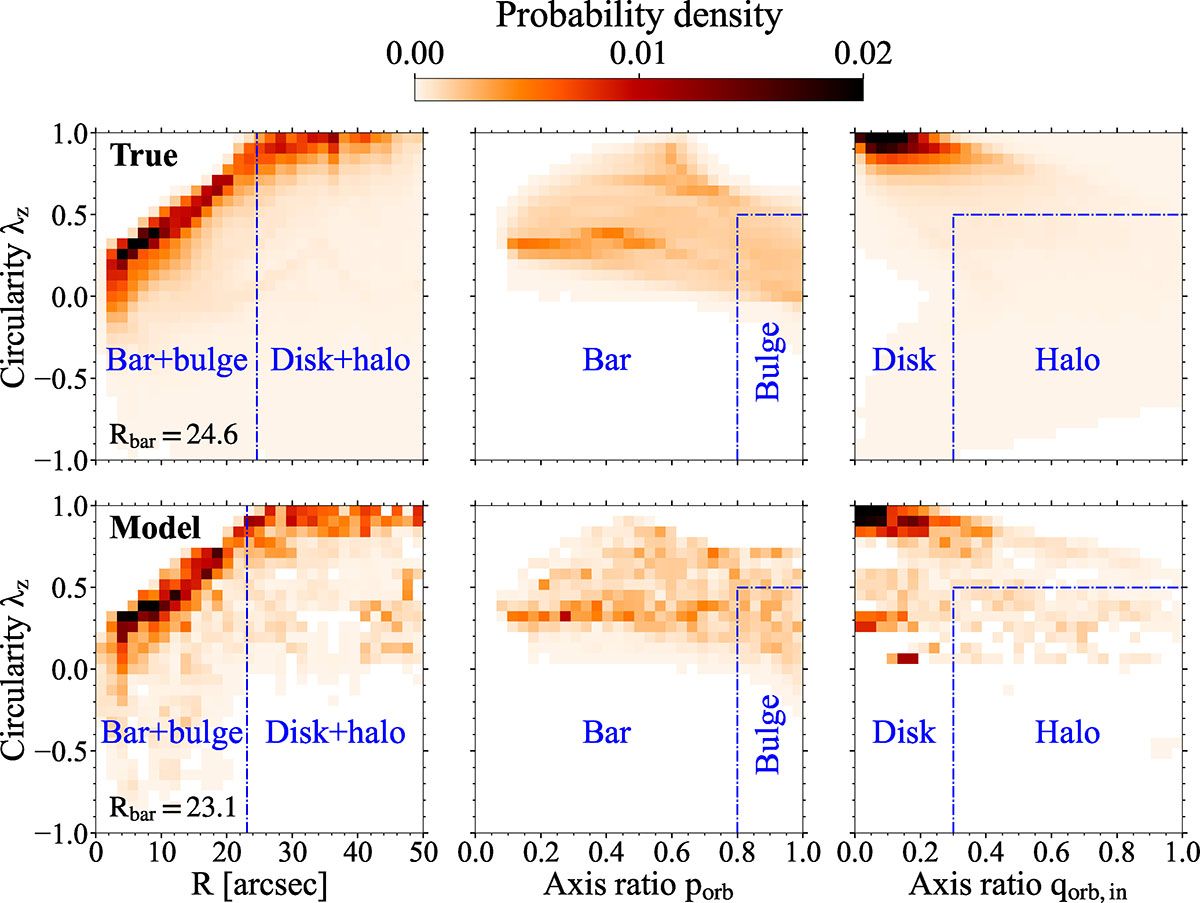
Structural decomposition based on orbital properties demonstrated using Au-23-85-50 and compared with the truth. Four properties are used to decompose the galaxy: Circularity, λz; time-averaged radius, R; axis ratio, porb, in the x-y plane; and axis ratio, qorb, in the x-z plane. The top panels display the true distributions while the bottom panels correspond to the model results. Left panels: Stellar orbit distributions of the entire galaxy in the λz–R phase space. We calculate the 1 kpc moving average of the cold orbit fraction fcold (λz ≥ 0.8; 1 arcsec = 0.2 kpc) and define the dynamical bar length, Rbar, as the smallest radius where fcold ≥ 0.5. Orbits with R ≤ Rbar are classified as bar+bulge components; those with R > Rbar are categorised as disc+halo components. The values of Rbar are indicated by the blue dashed lines and the annotations. Middle panels: Stellar orbit distributions for bar and bulge components in the λz–porb phase space. Orbits with λz ≤ 0.5 and porb ≥ 0.8 are assigned to the bulge; other orbits constitute the bar. The boundaries between the bar and bulge are shown by the blue dashed lines. Right panels: Stellar orbit distributions for disc+halo components in the λz–qorb, in phase space. Orbits with λz ≤ 0.5 and qorb, in ≥ 0.3 are categorised as the stellar halo; while the other orbits make up the disc. The boundaries between the disc and halo are shown by the blue dashed lines.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


