Fig. 3
Download original image
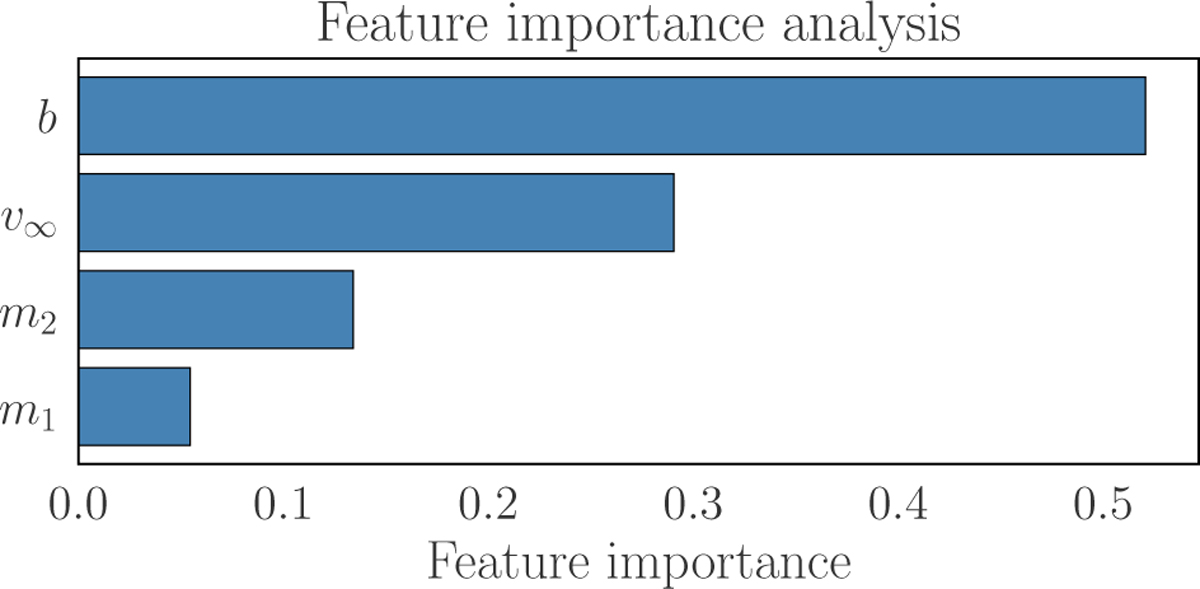
Parameter importance analysis reveals the relative contribution of each physical parameter to the model’s classification performance, with the impact parameter, b, exhibiting the strongest influence, followed by relative velocity, v∞, secondary mass, m2, and primary mass, m1. These importance scores are determined through the random forest algorithm’s internal metric, which quantifies how much each parameter decreases the Gini impurity across all decision trees in the ensemble. Specifically, the importance is calculated by: (1) summing the total impurity reduction achieved by splits involving each parameter across all trees; (2) normalising these values such that their sum equals unity; and (3) averaging over all trees. This process effectively measures how frequently and decisively each parameter is used to partition the parameter space. The y-axis reflects the normalised importance metric, meaning that higher values indicate greater discriminatory power in the classification.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


