Fig. 1.
Download original image
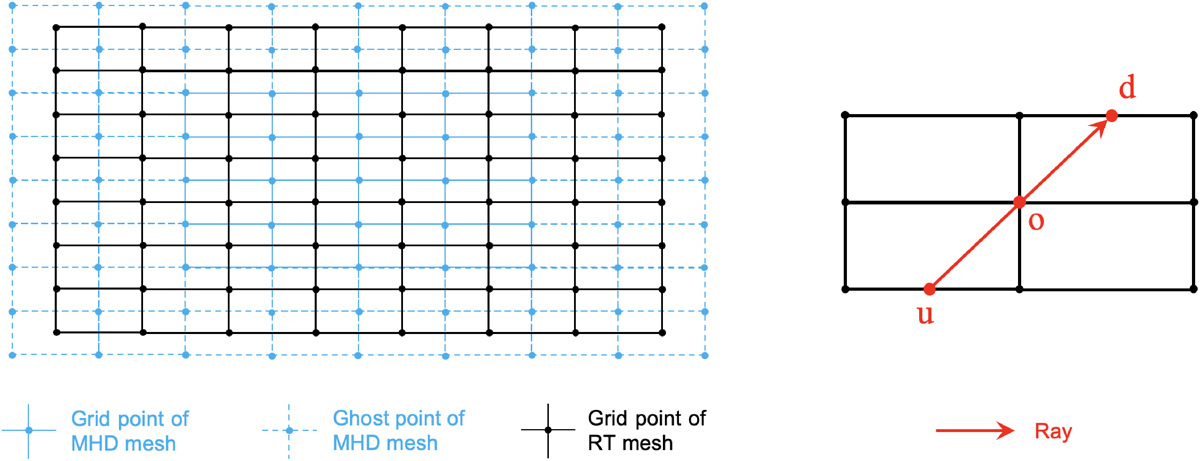
Schematic illustration of the mesh concerning RT. The left panel shows the computational meshes employed for solving the governing equations in the MURaM code, while the right panel illustrates the relationship between the radiation ray and the mesh structure. The MHD mesh is employed for solving the MHD equations, whereas the RT mesh is used for solving the RT equation. Both meshes are uniform and Cartesian, with the RT grid points positioned at the centers of the cells formed by adjacent MHD grid points. Information exchange between the two meshes is accomplished through bi-linear or tri-linear interpolation. Rays are involved in solving the RT equation using the short-characteristics method, in which the ray intensity at the grid points (o) is the quantity being solved for in MURaM. The solution involves the source functions at the upwind (u), downwind (d), and grid points, along with the ray intensity at the upwind point. The rays typically do not intersect with the grid vertices. Linear or bi-linear interpolation was employed to compute the source function, opacity, and ray intensity at the upwind and downwind points.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


