| Issue |
A&A
Volume 455, Number 2, August IV 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 441 - 451 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20042606 | |
| Published online | 04 August 2006 | |
Weak lensing measurements of dark matter halos of galaxies from COMBO-17
1
Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany e-mail: martina.kleinheinrich@uni-due.de
2
Institut für Astrophysik und Extraterrestrische Forschung, Universität Bonn, Auf dem Hügel 71, 53121 Bonn, Germany
3
Department of Physics, Denys Wilkinson Bldg., University of Oxford, Keble Road, Oxford, OX1 3RH, UK
4
School of Physics and Astronomy, Cardiff University, 5 The Parade, Cardiff, CF24 3YB, UK
5
Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, 14482 Potsdam, Germany
Received:
23
December
2004
Accepted:
19
April
2006
We present mass estimates for dark
matter halos around galaxies from the COMBO-17 survey using weak
gravitational lensing. COMBO-17, with photometry in 17 optical
filters, provides precise photometric redshifts and
spectral classification for objects with 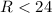 . This permits
to select and sort lens and source galaxies by their redshifts and lens
luminosity or color, which bypasses
many uncertainties in other weak lensing analyses arising from broadly
estimated source and lens redshifts. We study the shear created
by dark matter halos around 12 000 galaxy lenses at redshifts
. This permits
to select and sort lens and source galaxies by their redshifts and lens
luminosity or color, which bypasses
many uncertainties in other weak lensing analyses arising from broadly
estimated source and lens redshifts. We study the shear created
by dark matter halos around 12 000 galaxy lenses at redshifts
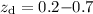 by fitting the mass normalization of either
singular isothermal spheres (SIS) or Navarro-Frenk-White (NFW)
profiles to background source orientations around the whole lens sample.
We also consider halos around
blue and red subsamples separately and constrain the scaling
of halo mass with light. For the NFW model, we find virial masses
by fitting the mass normalization of either
singular isothermal spheres (SIS) or Navarro-Frenk-White (NFW)
profiles to background source orientations around the whole lens sample.
We also consider halos around
blue and red subsamples separately and constrain the scaling
of halo mass with light. For the NFW model, we find virial masses
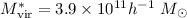 for blue and
for blue and 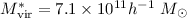 for red
galaxies of
for red
galaxies of 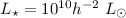 , respectively. The 1-σ
uncertainty on
, respectively. The 1-σ
uncertainty on 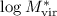 for the whole lens
sample is about 0.2.
We compare our results to those obtained from the Red-Sequence
Cluster Survey (RCS) and the Sloan Digital Sky Survey
(SDSS). Taking differences in the actual modelling into account, we
find very good agreement with these surveys.
for the whole lens
sample is about 0.2.
We compare our results to those obtained from the Red-Sequence
Cluster Survey (RCS) and the Sloan Digital Sky Survey
(SDSS). Taking differences in the actual modelling into account, we
find very good agreement with these surveys.
Key words: gravitational lensing / galaxies: fundamental parameters / galaxies: statistics / cosmology: dark matter
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


