Table A.1.
Mass estimates of R136a from single and binary stellar mergers for the winds described in this work.
| Method and Binarity | R136a1 | R136a2 | R136a3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MZAMS | Mcurrent | MZAMS | Mcurrent | MZAMS | Mcurrent | |
| Ṁrdw (Single) | 315 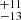 |
295 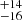 |
240 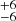 |
225  |
241 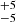 |
232 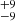 |
| Ṁrdw (Stellar merger) | 186 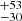 |
278 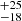 |
146 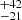 |
222 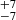 |
145 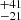 |
221  |
| ṀΓe (Single) | 389 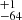 |
202 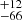 |
296 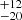 |
169 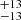 |
286 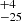 |
180 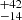 |
| ṀΓe (Stellar merger) | 207 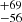 |
200 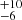 |
160 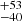 |
164 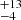 |
162 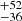 |
171 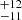 |
| ṀL/M (Single) | 359 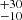 |
254 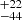 |
260 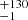 |
201 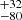 |
257 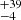 |
220 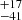 |
| ṀL/M (Stellar merger, Class 1) | 141 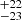 |
185 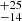 |
121 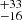 |
138 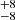 |
127 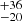 |
138 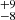 |
| ṀL/M (Stellar merger, Class 2) | 310  |
204 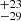 |
259 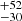 |
141 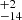 |
251 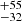 |
140 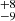 |
| Brands et al. (2022) | 273  |
222 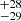 |
221 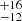 |
186 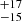 |
213 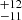 |
179 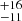 |
| Bestenlehner et al. (2020) | 251 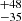 |
215 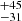 |
211 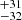 |
187 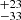 |
181 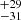 |
154 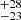 |
| Crowther et al. (2010) | 320 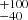 |
265 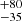 |
240  |
195 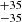 |
165 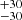 |
135 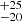 |
Notes. Column 1: The mass-loss recipe used and the origin of the star. Columns 2 and 3: ZAMS mass and current mass estimate of R136a1. Columns 4 and 5: ZAMS mass and current mass estimate of R136a2. Columns 5 and 6: ZAMS mass and current mass estimate of R136a3. In the case of a stellar merger, the MZAMS shows the mass of the primary star only. For stellar mergers computed with ṀL/M, we split the results into two mass regimes: primary mass below 200 M⊙ (class 1) and above 200 M⊙ (class 2), to account for the bimodal distribution. The last three rows present comparisons from the literature, all of which assume a single star origin. Crowther et al. (2010) results use the Geneva stellar evolution tracks, and the results from Bestenlehner et al. (2020) and Brands et al. (2022) both used the stellar models from Brott et al. (2011) and Köhler et al. (2015).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


