Fig. 11.
Download original image
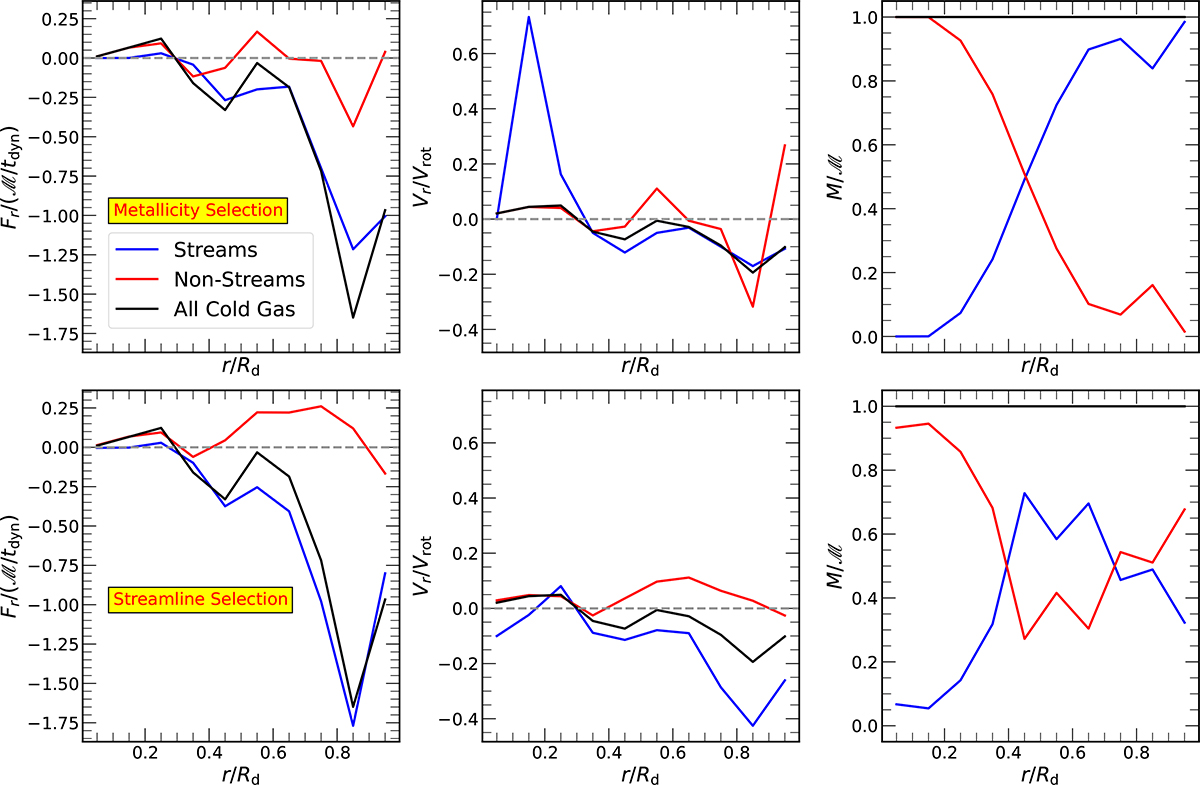
Stream and non-stream radial profiles. The left, middle, and right panels respectively show the radial mass flux (Fr, in units of ℳ/tdyn), average radial velocity (Vr, in units of Vrot), and mass (M, in units of ℳ), as functions of radius r, normalized by Rd, for all cold gas (black), streams (blue), and non-streams (red) in VELA 7 at z = 1.5. The top row presents results from the metallicity-based classification, and the bottom row corresponds to the streamline-based classification. In both cases, the total radial mass flux of cold gas is dominated by streams at large radii (beyond ∼0.7 Rd) and by non-streams at small radii (within ∼0.3 Rd). In the metallicity-based selection, the dominance of stream flux at large r primarily reflects the higher mass fraction of streams in that region. In contrast, the streamline-based method shows roughly equal masses for streams and non-streams at large r; however, the non-stream mass flux remains low. This is because the inflowing and outflowing contributions from non-stream gas nearly cancel out (see Fig. 10), leaving streams as the main net contributor to the total radial mass flux.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


