Fig. 2.
Download original image
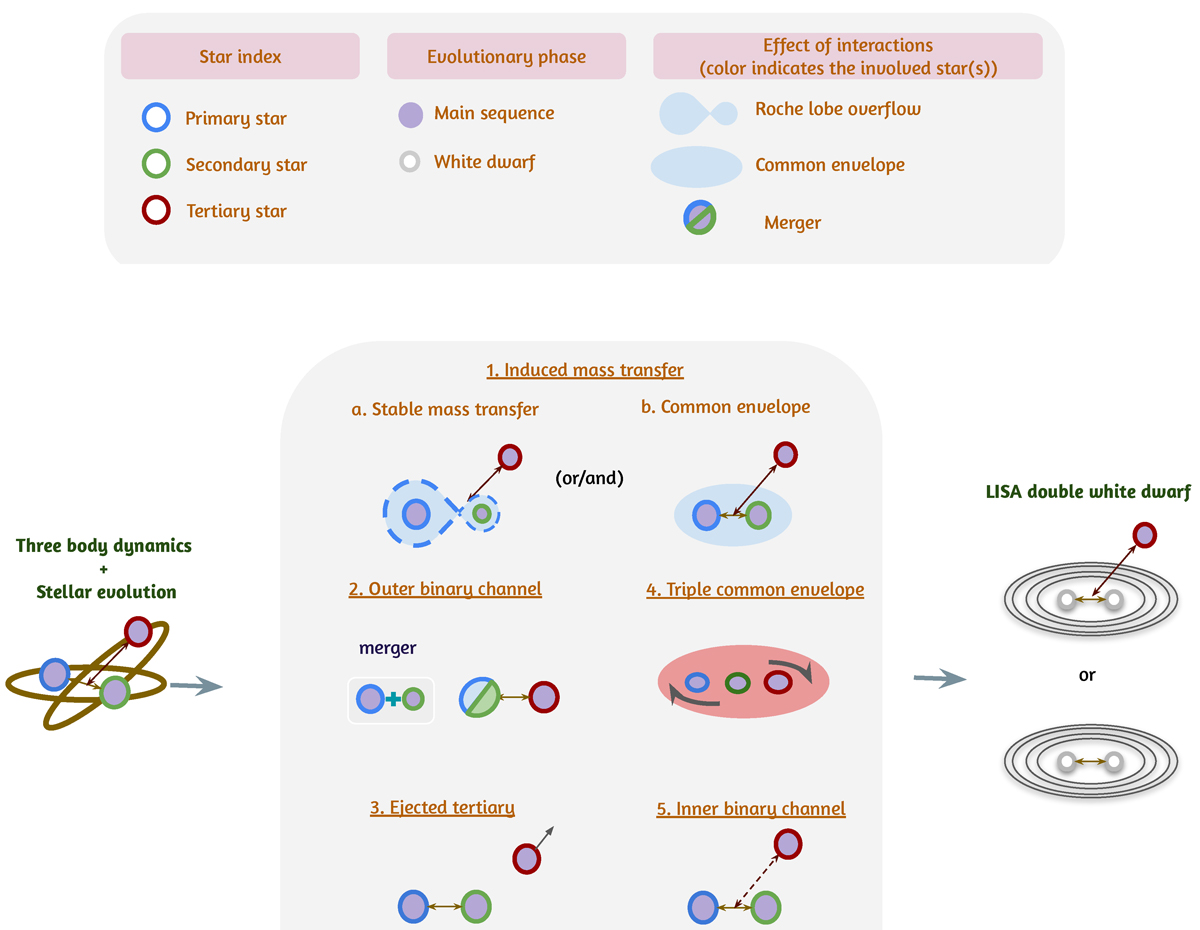
Diagram of possible key processes that drive the evolutionary phases of a triple evolution leading to the formation of a double white dwarf in the LISA frequency bandwidth. The diagram showcases key stages, including mass transfer, common envelope phases, ZLK oscillations that enhance eccentricity, and eventual binary evolution. The tertiary star plays a critical role in shaping the inner binary’s dynamics, either by inducing orbital changes or facilitating interactions that lead to the formation of the LISA double white dwarf. The circles represent the index of the star, with blue, green, and red indicating the primary, secondary, and tertiary stars, respectively. The filling inside each circle represents the star’s evolutionary phase: purple for the main-sequence and white for a white dwarf. A dashed arrow denotes a distant tertiary star that is too far to significantly influence the inner binary. A multi-colored circle represents a post-merger star, with the two colors signifying the components that have merged.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


