Fig. 1.
Download original image
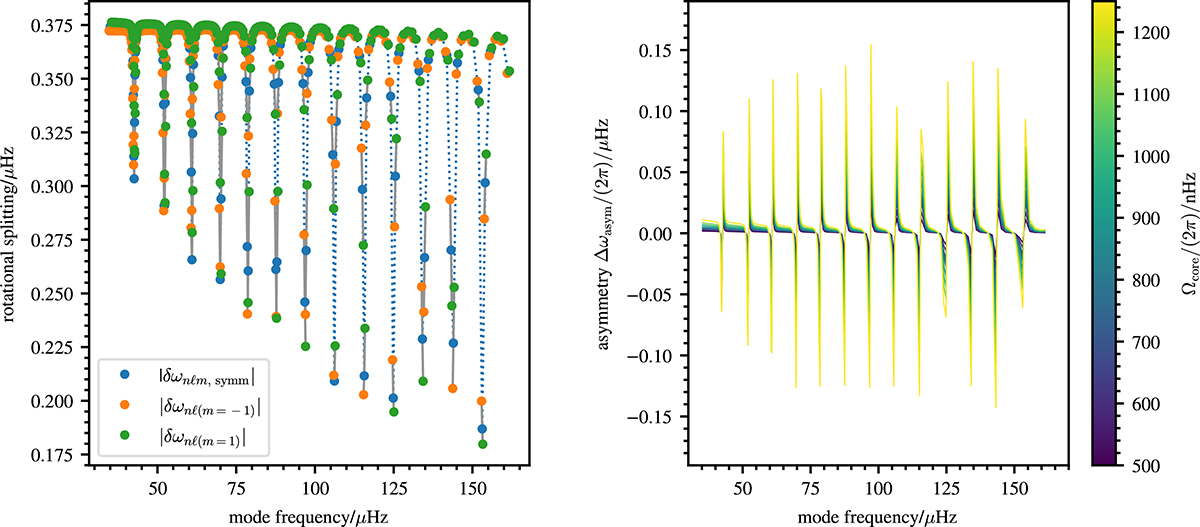
Rotational splittings and their asymmetries as a function of mode frequency. Left panel: Rotational splittings of the evolved model using a core rotation rate Ωcore/(2π) = 750 nHz and an envelope rotation rate Ωenv/(2π) = 50 nHz. Rotational splittings that have the same npg are connected by a grey line. Only a subset of the rotational splittings centred around νmax ≈ 100 μHz is selected for the rotational inversions (see text for details). The dotted blue line connects the symmetric splittings for clarity. The rotational splittings, δωnℓm, were obtained by computing the frequency differences according to Eqs. (13a) and (13b), using the frequencies obtained from solving the full QEP posed by Eq. (9), as described in Appendix C, while the symmetric rotational splittings, δωnℓm, symm, where obtained from Eq. (1). Right panel: Asymmetries of the rotational splittings (Δωasym) of the evolved model over a range of core rotation rates Ωcore, for Ωenv/(2π) = 50 nHz. The lines are colour-coded by the core rotation rate.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


