Table 4.
Deviations in H0 between simulations and tests.
| AvERA model | H0, model | H0 CC test | Deviation CC | H0 SN test | Deviation SN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AvERA-135k | 65.39 | 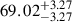 |
1.11σ | 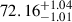 |
6.68σ |
| AvERA-320k | 68.91 | 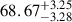 |
0.07σ | 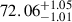 |
3.10σ |
| AvERA-625k | 71.38 | 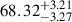 |
0.95σ | 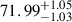 |
0.59σ |
| AvERA-1080k | 73.14 | 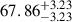 |
1.63σ | 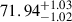 |
1.17σ |
Notes. H0 is given in kilometers per second per megaparsec. The deviations indicate the tension between the best-fit H0 values obtained from the CC and SN fits and the corresponding simulated H0, model values (Rácz et al. 2017) for each AvERA setting. While the CC test does not strongly favor any specific coarse graining scale, the SN test prefers higher particle numbers. Among the tested AvERA models, the 625k simulation shows the best agreement, with both CC and SN best-fit values lying within 1σ of the simulated H0, model.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


