Fig. 4.
Download original image
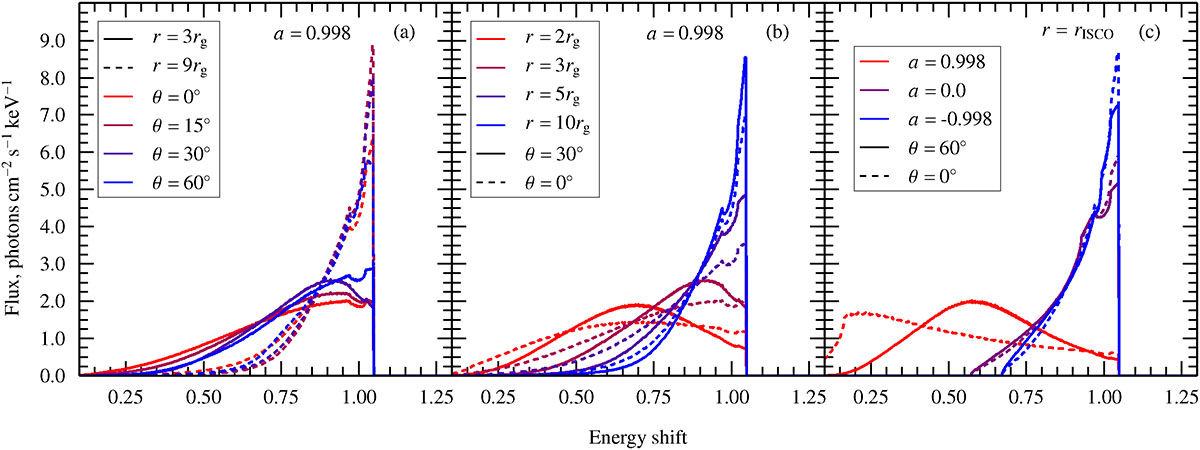
Line profiles for a ring geometry simulated with RELXILL. We display the geometric parameters of the ring in terms of spherical radii, r, and polar angles, θ. The parameters are uniquely related to height and ring radius through Eq. (4). For ease of comparison, we also convert these values to heights and radii in Table 1. (a) Varying polar angle of the primary source, θ, for two spherical radii, r = 3rg (dashed lines) and r = 9rg (solid lines), with a = 0.998. (b) Varying the spherical radius of the primary source, r, with two polar angles of the primary source, θ = 30° (solid lines) and θ = 0° (dashed lines, the lamp post case), with a = 0.998. (c) Varying the BH spin, a, for a source spherical radius fixed at ISCO value, r = rISCO, and θ = 60°. ISCO radii are 1.24rg, 6rg, 9rg for a = 0.998, 0.0, −0.998, respectively. To convert the quantities (r, θ) to (h, x), we provide the Table 1. All lines are normalized to have the same integrated photon flux. The photon index is Γ = 2 and the inclination to the observer is i = 30°.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


