Fig. 2
Download original image
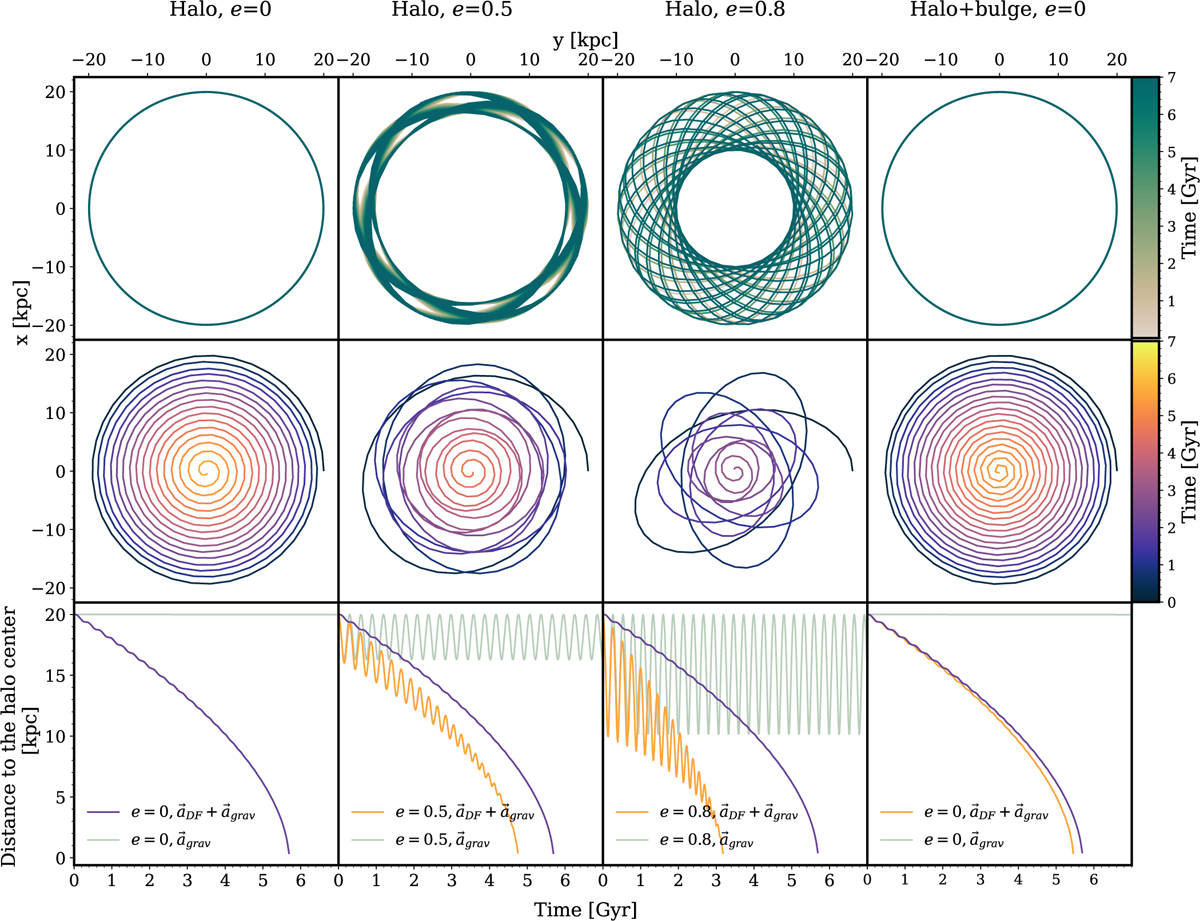
Evolution of a BH embedded in an NFW DM halo, with and without a central stellar bulge, as simulated using the OTIS code. The first three columns correspond to BH trajectories in an NFW halo with initial distance of 20 kpc from the halo centre and orbit ellipticities e = 0, e = 0.5, e = 0.8, while the fourth column includes a central bulge and shows the trajectory of the BH initially at 20 kpc and placed on a circular orbit. In the first and second rows, the trajectory color-code refers to the time elapsed since the beginning of the simulation, as indicated by the color map. Top row: BH trajectories when it is embedded within the static gravitational potential generated by the mass distribution, thus neglecting collisional effects from two-body encounters. Middle row: BH trajectories when collisional effects are included through the analytical description of the DF force (see Eq. (12)). Bottom row: time evolution of the BH’s radial distance from the halo centre. The green line shows the distance when aBH follows Eq. (5) (or Eq. (22) in the last column) mimicing the effect of a BH embedded in a collisionless medium. The purple line adds the DF contribution given by Eq. (12) for eccentricity e = 0, while the distance corresponding to the middle row of each panel is displayed by the orange curve.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


