Fig. 4.
Download original image
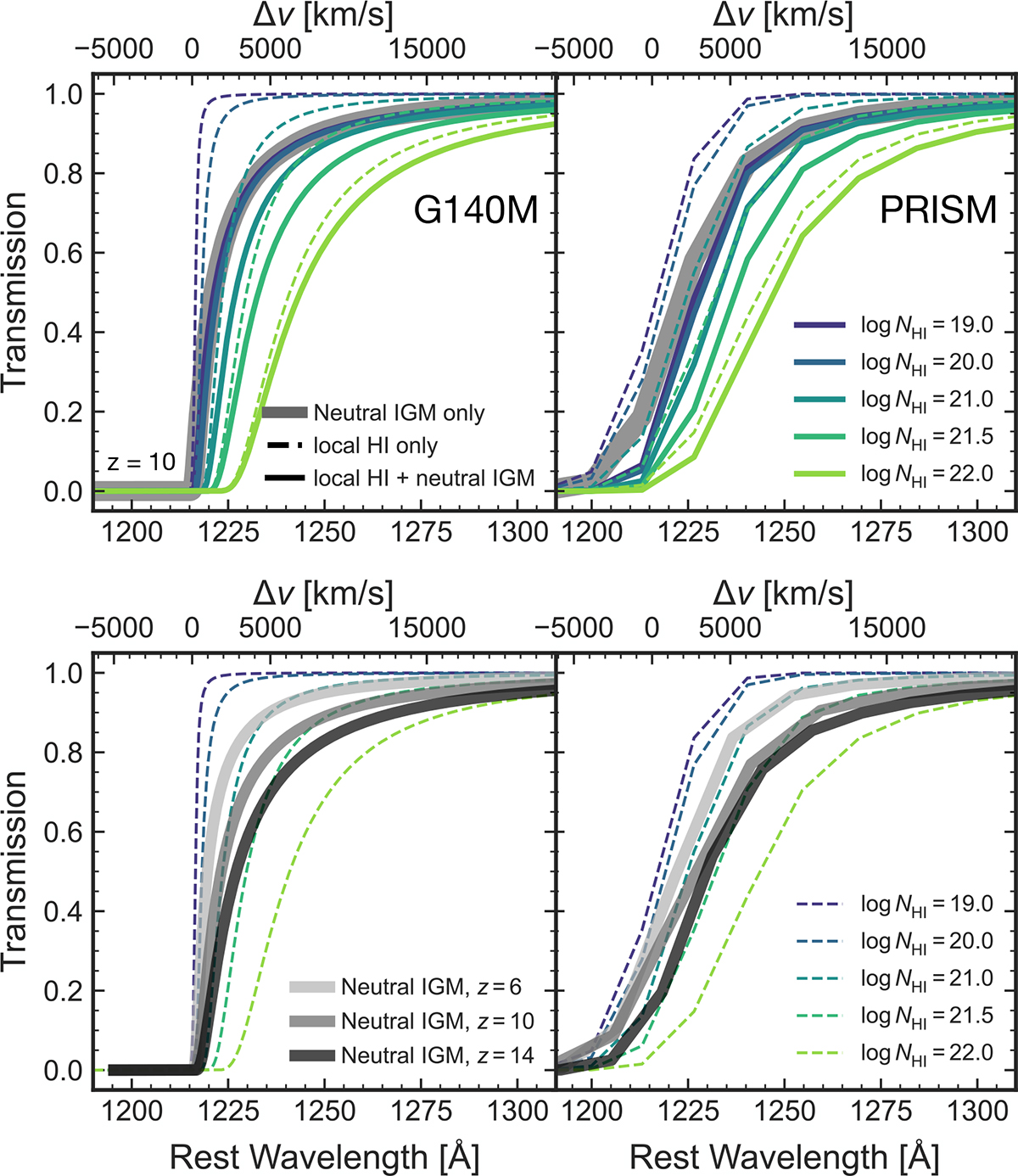
Transmission (e−τ) as a function of wavelength around Lyα due to the neutral IGM and local absorbers for high resolution (R ≳ 1000, left panels) and convolved with the resolution of the prism (right panels). Top panels: Transmission for a source at z = 10. The thick grey line shows the transmission expected in the fully neutral IGM (Section 2.1.1). Dashed coloured lines show the absorption profiles expected for local absorbers in an ionized IGM (Section 2.2). Solid coloured lines show the profiles for the combinations of both local absorbers and neutral IGM. For NH I ≲1020.5 cm−2 the neutral IGM dominates the damping wing profile. For higher column densities NH I ≳ 1022 cm−2, the shape becomes dominated by the local absorption, though the neutral IGM causes more absorption at redder wavelengths than a local absorber alone. Bottom panels: Neutral IGM damping wing at z = 6, 10, 14 (grey solid lines) compared to only local absorption (dashed coloured lines, same as top panel). By z ∼ 14 the IGM damping wing becomes similar in strength to a NH I ≳ 1021.5 cm−2 local absorber.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


