Fig. 5.
Download original image
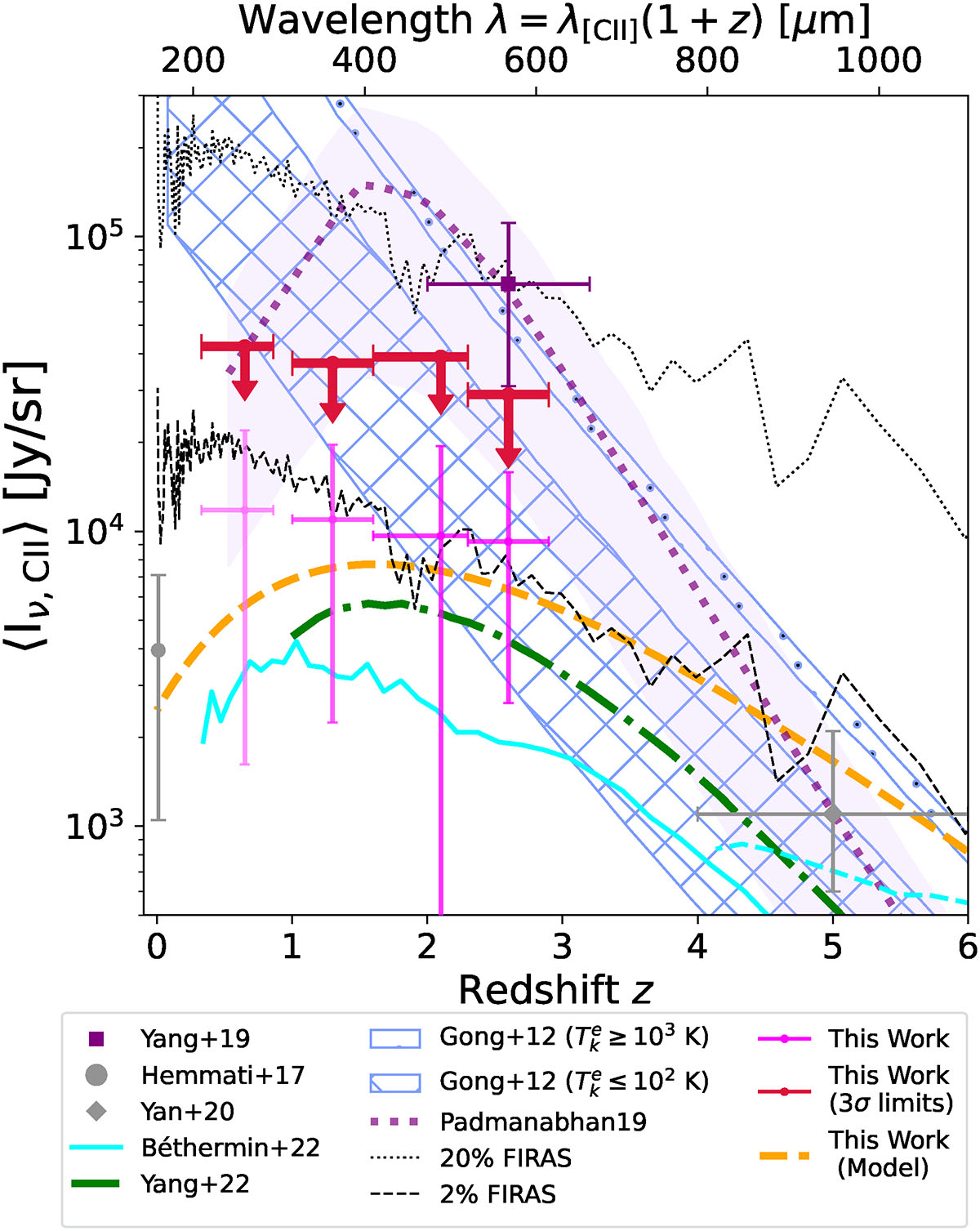
Measurements of [CII]-158 μm at z ∼ 0.3 − 2.9 compared with [CII]-158 μm-LF estimates in the local universe (Hemmati et al. 2017) and z ∼ 5 (Yan et al. 2020). Also shown are theoretical predictions from C+ evolution models, including Gong et al. (2012) (blue hatches), Padmanabhan (2019) (dotted purple: best model, shaded band: uncertainty), Yang et al. (2022) (dash-dotted green), and Béthermin et al. (2022) (cyan line: De Looze et al. 2014 version; cyan dashed: high SFRD version at high z). Our 3σ upper limits disfavor high-temperature collisional excitation frameworks and best-fit empirical models calibrated to the Pullen et al. (2018), Yang et al. (2019)Planck measurement. The 1σ results are more consistent with SFR-scaling models, which calibrate C+ luminosity to the SFR of sources. Additionally, we show the COBE/FIRAS measurement of the monopole spectrum of the CIB as a function of wavelength, matched to the rest-frame redshift of [CII]-158 μm emission. The [CII]-158 μm contribution is likely no more than a few percent of the total CIB, with the intensity history evolving by less than an order of magnitude across cosmic moon.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


