Fig. D.4.
Download original image
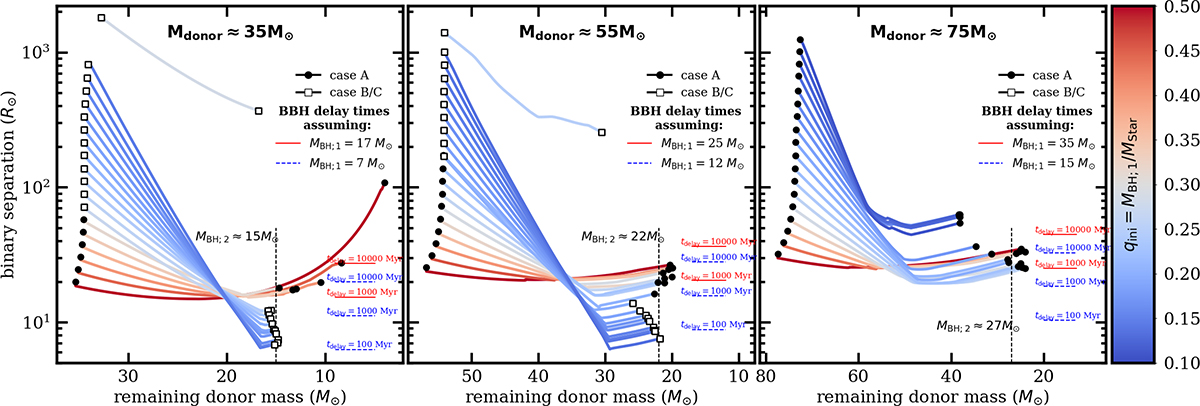
Evolution of binary separation during the mass transfer phase in MESA models of BH+O-star systems with q = qcrit mass ratios and initial O-star masses of 35, 55, and 75 M⊙ (the three different panels), plotted as a function of the decreasing remaining donor mass. Different lines correspond to different initial separations, colored by the initial mass ratio Mdonor/Maccretor. The initially more narrow systems interact when the donor is a MS star (closed circles), whereas in wider orbits the interaction is from a post-MS donor (open squares). Because the mass ratio is critical for each mass and radius of the donor at RLOF, the models shown here lead to the smallest binary separations via SMT evolution given the donor. See Fig. 5 for a full parameter space exploration, with other initial donor masses and radii. Assuming that at the end of its evolution the donor collapses to form a BH with mass 15, 22, and 27 M⊙ (for different panels), we mark which binary separations would be required for BBH delay times of 100, 1000, or 10000 Myr for BBH mass ratio 0.9. Counter-intuitively, the smallest separations and the shortest BBH delay times from the SMT channel may originate from initially the widest BH+O-star systems (post-MS donors in the 35 and 55 M⊙ panels).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


