Fig. 2.
Download original image
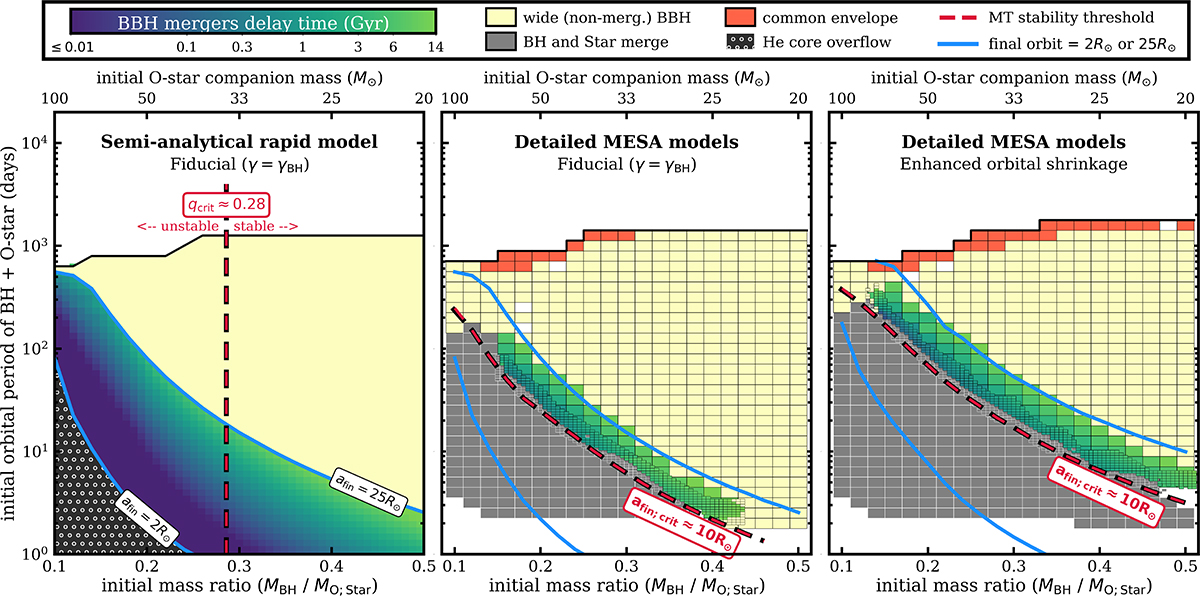
Window for the formation of BBH mergers as predicted by semi-analytical and detailed binary models. Colors mark the evolutionary outcomes of interacting BH+O-star systems across different initial periods and mass ratios, calculated with our semi-analytical rapid model of SMT evolution (left panel; Sect. 2.3) and compared with MESA binary models for two different assumptions on orbital shrinkage during mass transfer: fiducial (γ = γBH, center) and enhanced shrinkage due to L2 outflows (right). The initial BH mass is always MBH; 1 = 10 M⊙ and metallicity is Z = 0.1 Z⊙ (see Fig. D.1 for other BH masses). Wide-non interacting systems are not shown. Solid blue lines mark systems in which the SMT evolution would lead to final orbital separation afin = 2 R⊙ or 25 R⊙, according to the semi-analytical model, which is approximately the range of separations needed for BBH mergers. The dashed red line is the boundary between stable and unstable mass transfer. The outcomes of the semi-analytical model are only applicable if the mass transfer is stable. In rapid codes, it is typically assumed to be related to a critical mass ratio (the vertical line at qcrit ≈ 0.28, left panel). In the MESA models, the stability is determined self-consistently at every timestep, and it is found to be entirely different. The mass transfer only remains stable in systems where the final separation is afin ≳ 10 R⊙. This conclusion is robust against uncertainties of SMT evolution and holds even if enhanced orbital shrinkage is assumed (right), leading to BBH mergers with long delay times ≳1 Gyr (Sect. 3.4).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


