Fig. 9.
Download original image
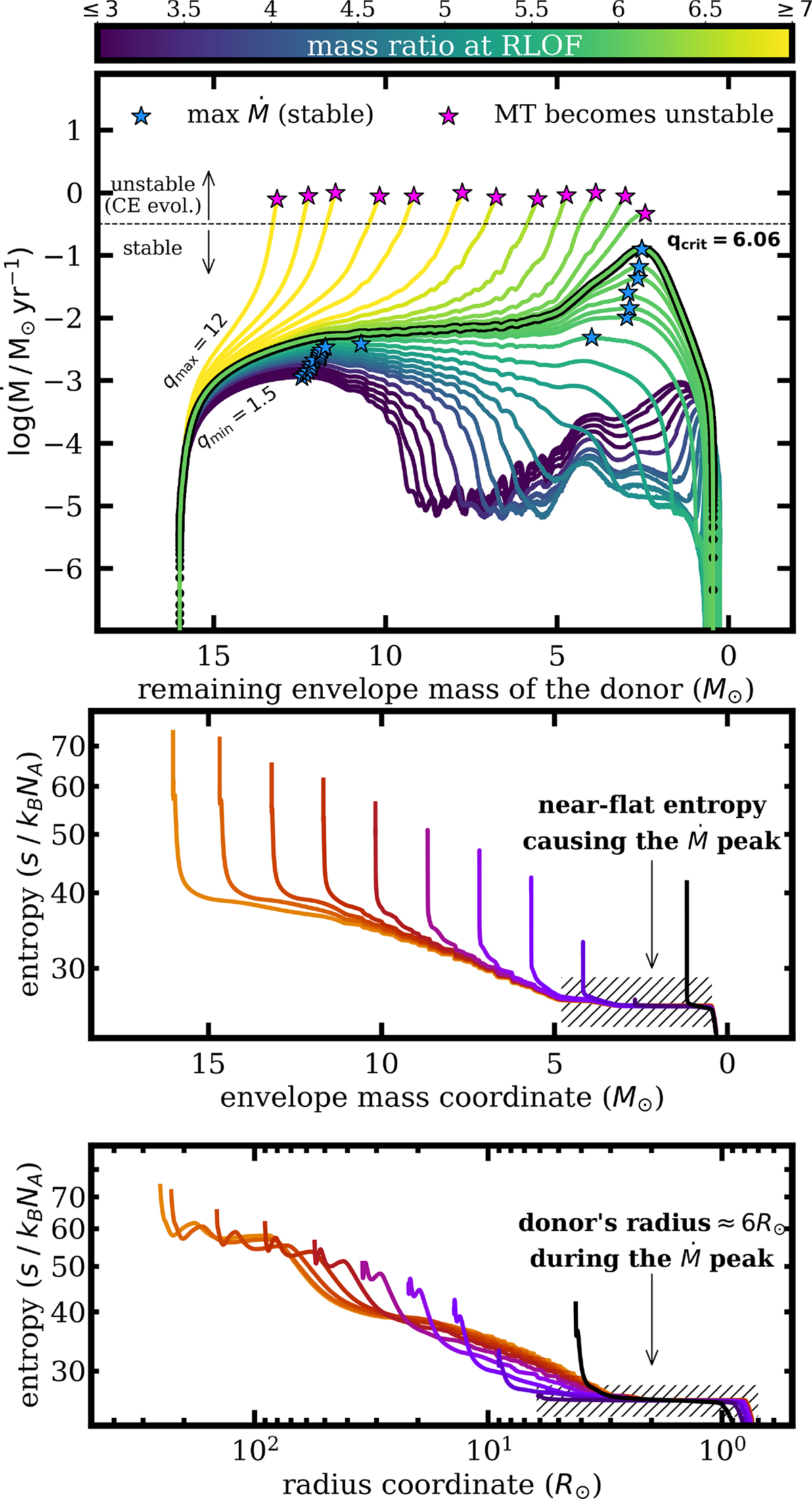
Origin of the separation limit lies in delayed dynamical instability. Top: Mass transfer rate (Ṁ) in systems with a 30 M⊙ donor and a varying mass ratio at RLOF, shown as a function of the decreasing envelope mass. The donor is the same for each mass ratio at the onset of RLOF: ∼250 R⊙ core-He burning giant with a ∼17 M⊙ envelope and ∼13 M⊙ core. Models reaching log(Ṁ/M⊙ yr−1) > 0.5 become unstable (Sect. 2.4), as indicated by the dashed horizontal line. The critical mass ratio for stability is qcrit = 6.06 (marked in bold). The threshold between stable and unstable models is determined by the Ṁ peak at Menv ≈ 2.5 M⊙. Middle: Internal entropy profiles of the donor in the q = qcrit model, ranging from the onset of RLOF (light, left) to the end of mass transfer (dark, right). The Ṁ peak seen in the top panel is caused by stripping off the layers where the entropy profile is nearly flat. Bottom: The same entropy profiles but as a function of the radius coordinate. The flat entropy layers are within the inner 3 R⊙ of the donor (6 R⊙ during the Ṁ peak), causing instability in models in which the mass transfer would shrink the orbit below a ≲ 8 R⊙.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


