Fig. F.2
Download original image
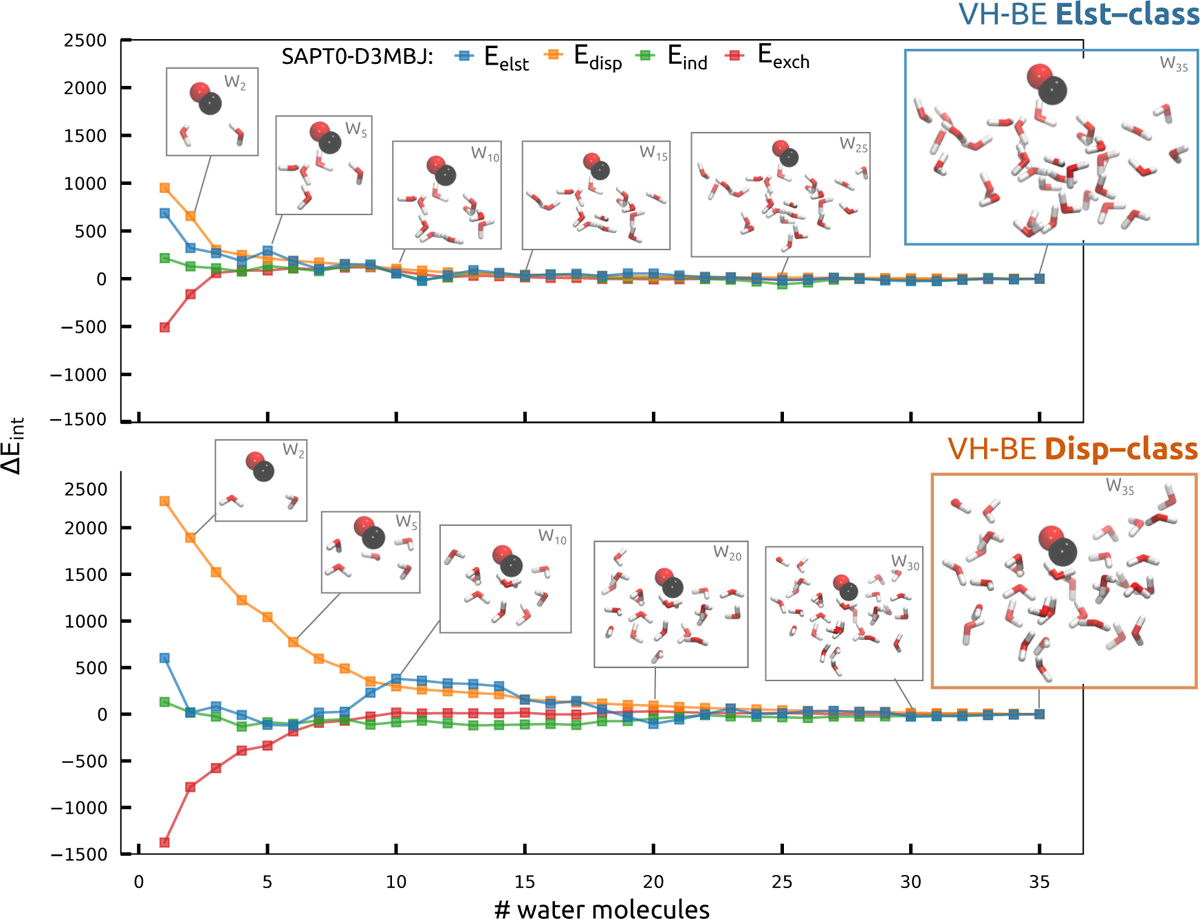
Convergence of SAPT0-D3MBJ interaction energy components for CO as a function of binding site size. The plot is generated by incrementally adding water molecules to CO from an extracted VH-BE Elst-class binding site (upper panel) and a VH-BE Disp-class binding site (lower panel). The interaction energy difference are with respect of the CO + W35 limit (∆Eint = Eint(CO + W35) − Eint (CO + WX). The interaction energy in the Elst-class converges significantly faster than in the Disp-class binding site. The interaction energy is further decomposed into electrostatic, induction, dispersion and exchange contribution, of which the dispersion interaction is the slowest to converge. Therefore, selecting a binding site extract comprising 28 water molecules captures almost the totality of the interaction energy of CO + ASW.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


