Fig. 3.
Download original image
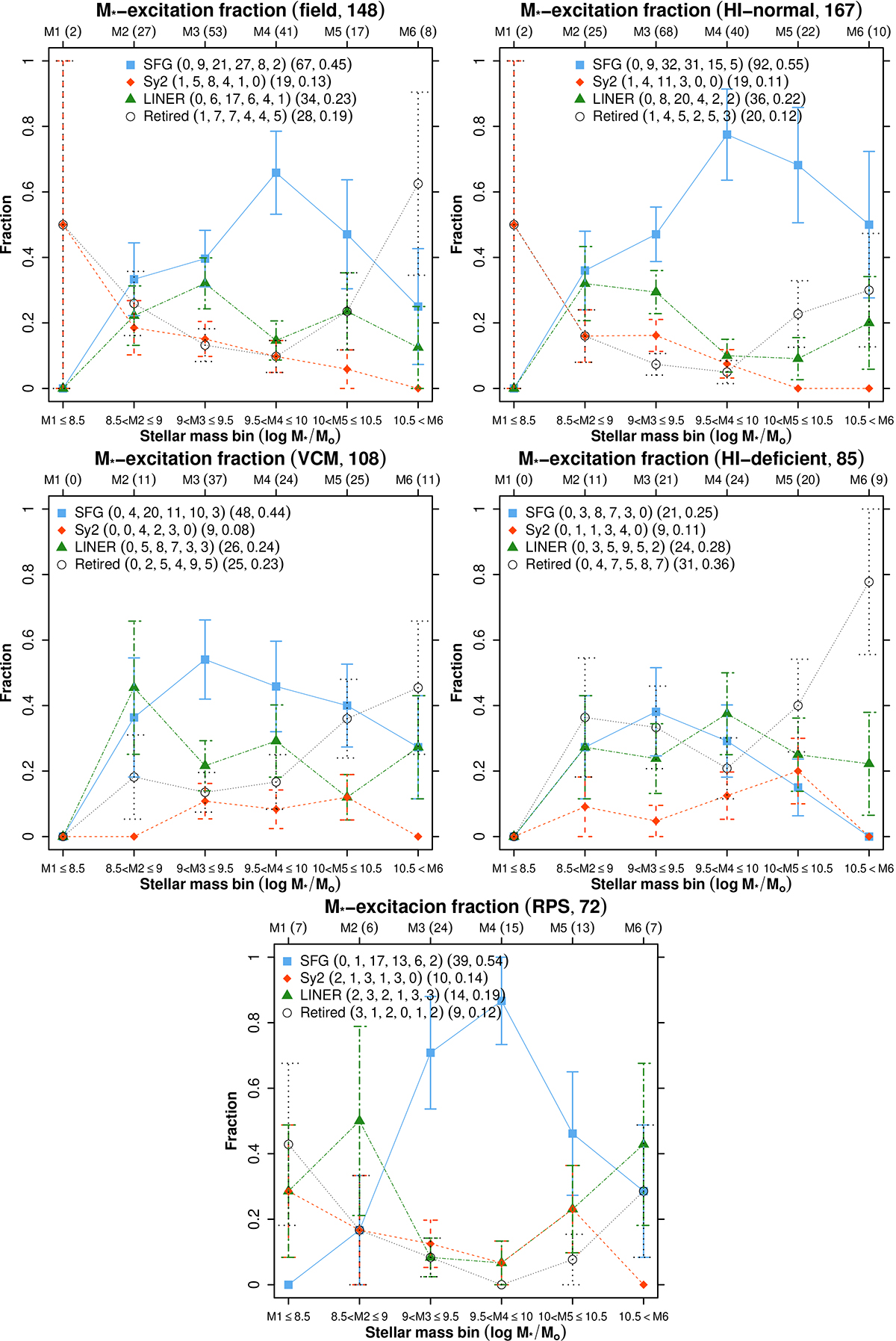
Stellar mass-excitation fraction relation. Excitation types are based on mid-infrared colour diagnostics (mIRdds) representing central apertures (median size ∼3.12 kpc for the HRS). Section 2.1 details the HRS environmental classification. Stellar masses are binned from low to high (left to right): log (M*/M⊙), M1 ≤ 8.5, 8.5 < M2 ≤ 9.0, 9.0 < M3 ≤ 9.5, 9.5 < M4 ≤ 10.0, 10.0 < M5 ≤ 10.5, and 10.5 < M6. Top: Field and H I-normal galaxies. Middle: Virgo cluster members (VCMs) and H I-deficient galaxies. Bottom: Objects undergoing RPS in nearby clusters. Total galaxy counts are shown in the panel titles. Each panel lists excitation-type counts per mass bin (from left to right), with total counts and respective fractions shown on the rightmost side. The x axis labels indicate galaxy counts per stellar mass bin (top). Random uncertainties, indicated by vertical bars, are expressed as the ratio of the square root of each excitation-type count to the total. See also Tables 2, D.1, and D.2.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


