Fig. 7.
Download original image
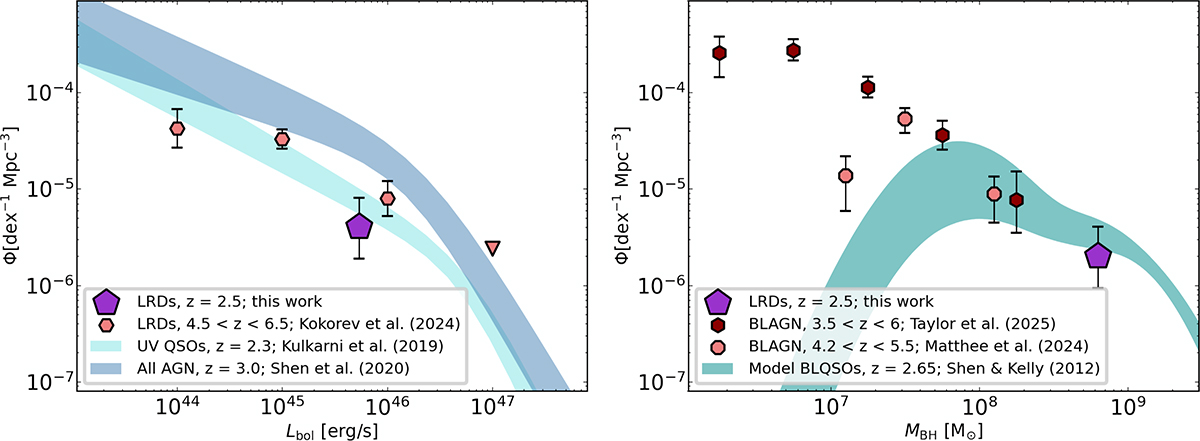
Left: space density of LRDs at Lbol, mean = 5.4 × 1045 erg s−1 and zmean ∼ 2.5 from our work (purple pentagon) compared with the bolometric luminosity function derived at similar redshifts for the entire AGN population (steel blue; Shen et al. 2020) and for blue, UV-selected, unobscured AGNs (pale turquoise; Kulkarni et al. 2019). The shaded areas correspond to the 16th and 84th percentiles of the bolometric LFs. At cosmic noon, the measured abundance of LRDs appears to be a factor 2 − 3 lower than that of unobscured AGNs. We also compare our estimate with the bolometric luminosity function of LRDs at 4.5 < z < 6.5 from Kokorev et al. (2024) (in red). Right: space density of LRDs at zmean ∼ 2.5 and MBH ∼ 6.3 × 108 M⊙ (purple) compared with the predicted active BHMF from broad line quasars at similar redshift (dark cyan; Shen & Kelly 2012) and the active BHMF of LRDs at higher redshifts (red symbols, Matthee et al. 2024; Taylor et al. 2025). The shaded area corresponds to the 16th and 84th percentiles of the model active BHMF value.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


